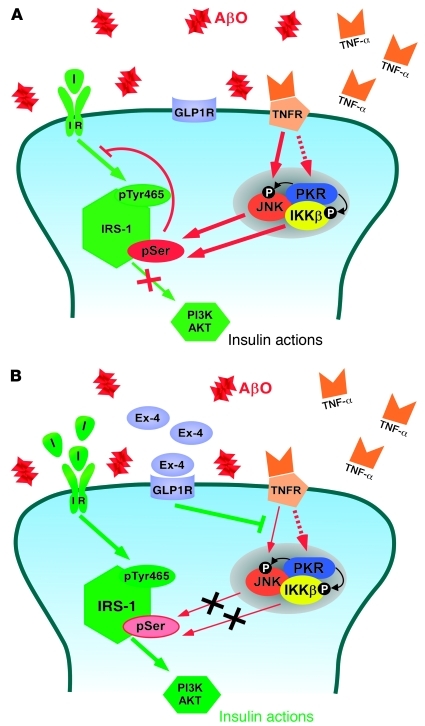
Figure 9. Proposed mechanism underlying disrupted brain insulin signaling in AD.
(A) AβOs stimulate TNF-α signaling, which activates the JNK pathway and, possibly, PKR and IKK pathways. Activation of these stress-sensitive kinases, which can also be triggered by endoplasmic reticulum stress (36), results in serine phosphorylation of IRS-1, blocking downstream insulin signaling. (B) Stimulation of insulin and GLP1 receptors blocks AβO-induced defects in insulin signaling. Binding of exendin-4 to GLP1 receptors and of insulin to IRs prevented activation of JNK, allowing physiological tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1 and stimulating downstream insulin signaling. In both panels, red arrows indicate inhibitory pathways and green arrows indicate stimulatory pathways of insulin signaling. I, insulin.