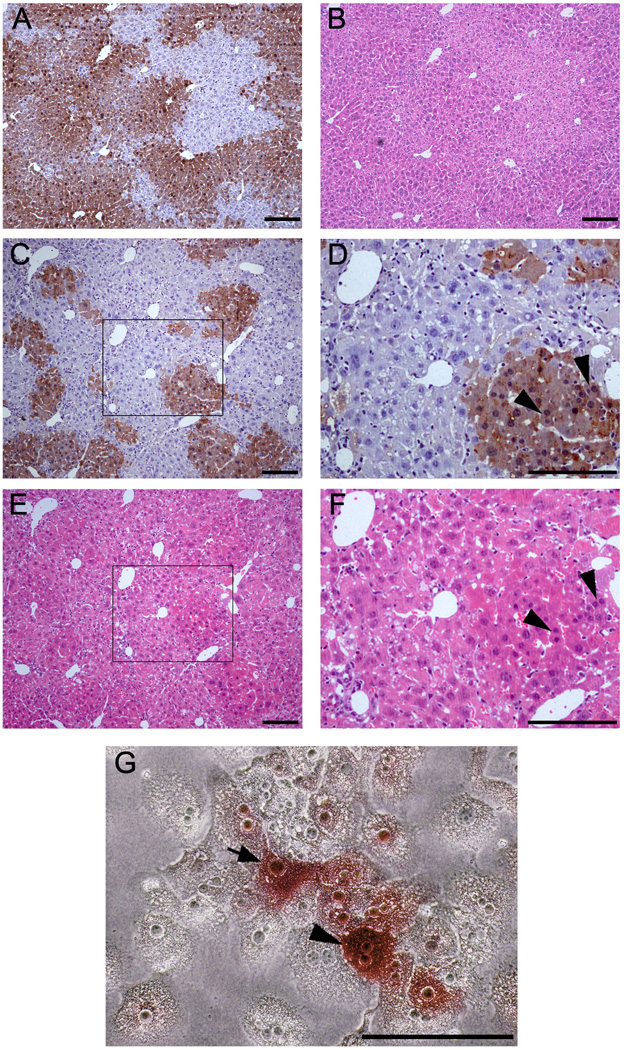
Figure 4. Morphological characters of ES cells derived hepatocytes engrafted in the liver structure after liver repopulation in secondary recipients and in culture after perfusion.
(A, B) Wild-type hepatocytes after liver repopulation in Fah−/− mouse recipient as control. A: anti-FAH immuno-staining; B: H&E staining. (C–F) Like with wild-type hepatocytes, ES cell-derived hepatocytes engrafted into liver sinusoids in the Fah−/− mouse recipients. C and D: anti-FAH immuno-staining; E and F: H&E staining. D and F highlighted the areas inside C and E. (G) Morphological characteristics of ES cell-derived hepatocytes in vitro. ES cell-derived hepatocytes were positive for FAH, showed the typical hepatocyte morphology in culture, shown with FAH-negative hepatocytes of Fah−/− mice after liver perfusion. (Arrowhead and arrow were used to indicate the FAH-positive hepatocyes with bi-nuclear or mono-nuclear, respectively). Scale bars: 200 µm (A–F), 100 µm (G).