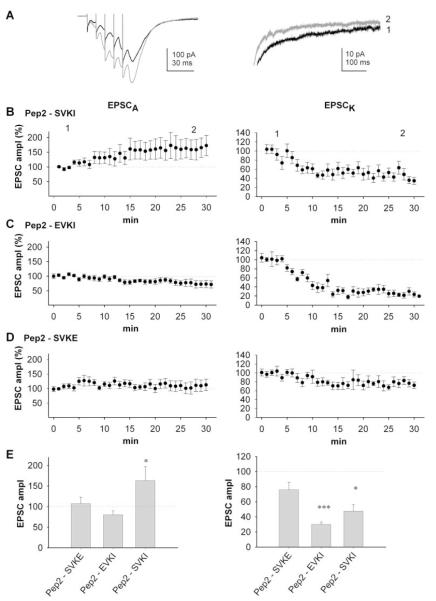
Figure 6.
Rapid, Differential Regulation of AMPAR- and KAR-Mediated Synaptic Transmission by PDZ Proteins
(A) EPSCs evoked by five shocks at 100 Hz obtained 3 min (black traces) and 25 min (gray traces) following obtaining whole-cell access with intracellular pep2-SVKI. Note the increase in EPSCA and decrease in EPSCK, which is more clearly seen in the expansion of the EPSC decay (right-hand trace).
(B) Pooled data (n = 14) of amplitude of EPSCA and EPSCK for neurons infused with pep2-SVKI.
(C) Pooled data (n = 9) of amplitude of EPSCA and EPSCK for neurons infused with pep2-EVKI.
(D) Pooled data (n = 9) of amplitude of EPSCA and EPSCK for neurons infused with pep2-SVKE.
(E) Summary data for EPSCA (left panel) and EPSCK (right panel) from the same experiments, taken at 30 min.