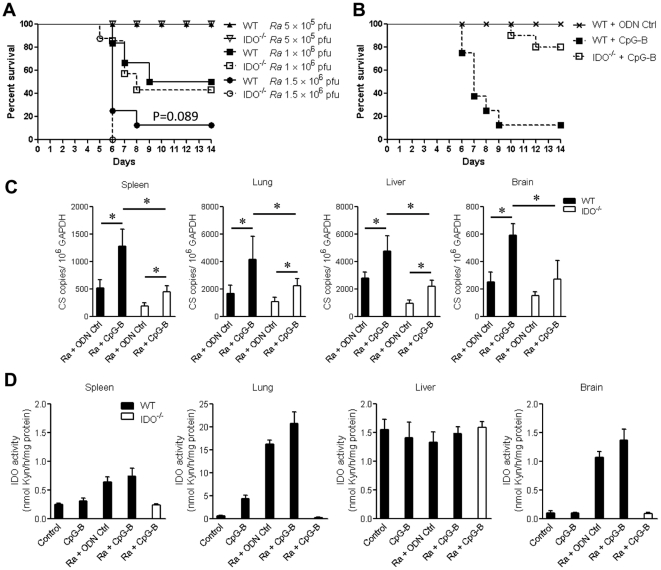
Figure 2. CpG-B induced death of R. australis-infected mice through IDO.
WT and IDO−/− mice (6–8 mice per group) were injected i.v. with different doses of R. australis. Mouse survival was monitored for 14 days (A). 50 µg of ODN control (ODN 1826 control) or CpG-B (ODN 1826) per mouse were injected i.v. into B6 and IDO−/− mice (8 mice per group) at day 2 after infection with 5×105 pfu of R. australis, respectively. Mouse survival was monitored for 14 days (B). Tissue bacterial loads determined by realtime PCR (C) and tissue IDO enzymatic activity determined by modified colorimetric assay (4 mice per group) were measured on day 5 post-infection (D). The representative results are shown as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. * p<0.05.