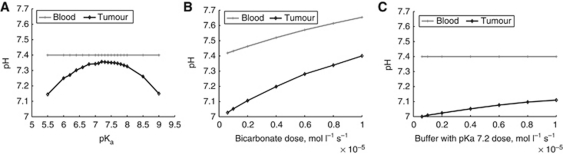
Figure 6.
Predicted optimal pKa of a hypothetical buffer and comparative efficacy. (A) The optimal pKa is between the pHe of the tumour and tissue. In this case, the optimal pKa is 7.2, directly between the tumour pHe of 7.0 and the blood pHe of 7.4. (B) Simulated blood and tumour pHe with bicarbonate of various doses (horizontal axis) in a human. Note the elevation in both blood and tumour pHe with bicarbonate. (C) Simulated blood and tumour pHe with a buffer of pKa 7.2 titrated to pHe 7.4. As predicted, the hypothetical buffer titrated to pHe 7.4 does not raise the blood pHe (in contrast to administration of bicarbonate). In both (B and C), the tumour pHe is elevated, but bicarbonate at the equivalent dose has a larger effect on both blood and tumour pHe.