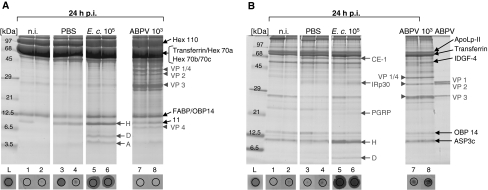
Fig. 4.
Comparison of humoral immune responses of bee larvae and adults upon bacterial and viral infections. Fourth-instar larvae (A) or newly emerged worker bees (B) were either left untreated (n.i.), mock-infected with PBS, or challenged with 105 E. coli cells or with 103 ABPV particles. Haemolymph samples were collected 24 h p.i., followed by protein analysis and inhibition-zone assays. Aliquots of 1.5 μl were applied to 15% PAA/0.1% SDS gels containing tricine (A) or no tricine (B). Aliquots of the same samples were applied to agar plates together with M. flavus as indicator bacteria. Newly synthesized ABPV-specific capsid proteins are indicated by red arrowheads. The AMPs hymenoptaecin (H), defensin 1 (D), abaecin (A) and the immune-responsive proteins carboxylesterase (CE-1), IRp30 and peptidoglycan recognition protein-S2 (PGRP) induced upon bacterial infection [41] are marked by red arrows. The corresponding bands were excised from the gels, and the proteins were identified by subsequent MS/MS analysis (colour figure online)