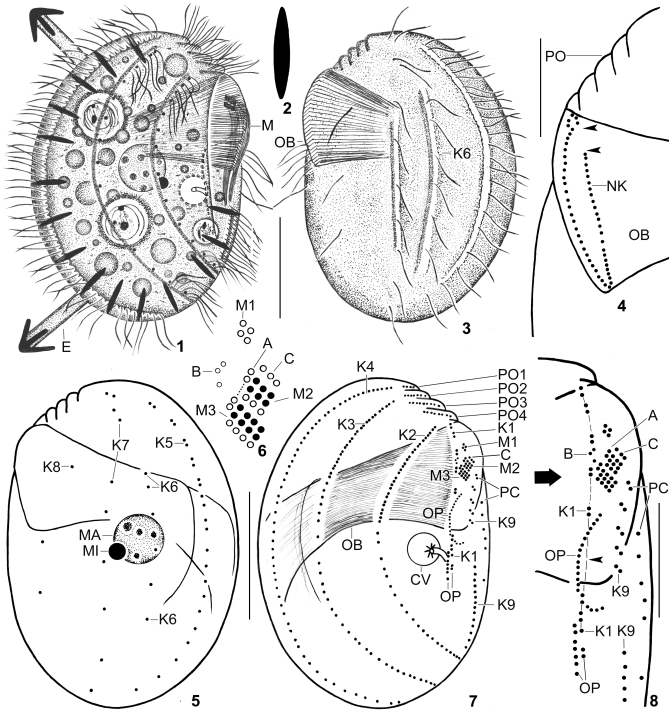
Figs 1–8.
Leptopharynx brasiliensis from life (1–3) and after protargol impregnation (4–8). 1, 3. Right and left side view of representative specimens. Note the margin of a hyaline plate on the ventral side (hatched line), the left side ciliation, the two furrows extending on the left side and containing kinety 6 as well as the middle portion of kinety 7, the distinctly oblique preoral region, and the large oral basket. 2. A resting extrusome, 6–7 μm long. 4. Left side view of the oral basket opening, showing the break of the nasse kinetosomes in the left anterior portion (arrowheads) and the curl-like pattern at the right end. 5–8. Left and right side view (5, 7), adoral membranelles (6), and the arrangement of the basal bodies on the ventral side (8) of the holotype specimen, length 52 μm. The hatched line in (8) connects the basal bodies of kinety 1. Note the wide break between the fifth and sixth dikinetid (arrowhead). Open circles in (6) indicate non-ciliated basal bodies. A, group A basal bodies; B, group B granules; C, group C basal bodies; CV, contractile vacuole; E, exploding extrusome; K1–9, somatic kineties; M(1–3), adoral membranelles; MA, macronucleus; MI, micronucleus; NK, nasse kinetosomes; OB, oral basket; OP, oral primordium; PC, postoral complex; PO (1–4), preoral kineties. Scale bars 20 μm (1, 3, 5, 7), and 10 μm (4, 8).