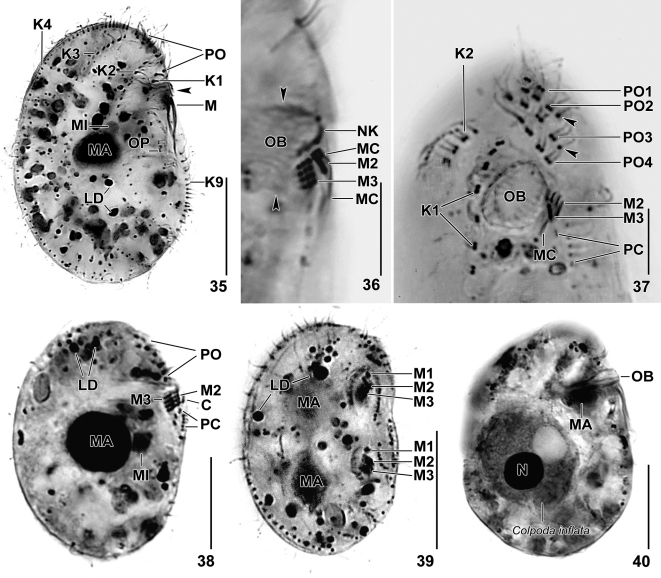
Figs 35–40.
Leptopharynx costatus gonohymen after protargol impregnation. 35, 36. Right side view of the hapantotype specimen for the large morph. Note the right-angled M2 and M3, shown at higher magnification in (36). Arrowheads denote the narrow oral basket. 37. Ventral view of a paratype specimen, showing the right-angled M2 and M3, the broadly elliptical oral basket opening, the widely spaced kinetids of kinety 1, and the preoral kineties. Arrowheads mark the monokinetids at end of preoral kineties 2 and 3. 38. Right side view of the hapantotype specimen for the small morph, having the same body shape and oral apparatus (flat adoral membranelles) as the small morph of L. costatus costatus. 39. Right side view of a divider of the small morph, showing the three adoral membranelles in both proter and opisthe. 40. Right side view of a large morph specimen. Although having a narrow oral basket, it can ingest large prey, viz., Colpoda inflata. Note the anteriorly dislocated macronucleus. C, group C basal bodies; K1–4, 9, somatic kineties; LD, lipid droplets; M(1–3), adoral membranelles; MA, macronucleus; MC, membranellar cilia; MI, micronucleus; N, macronucleus of prey ciliate, Colpoda inflata; NK, nasse kinetosomes; OB, oral basket; OP, oral primordium; PC, postoral complex; PO(1–4), preoral kineties. Scale bars 20 μm (35, 40), 15 μm (38, 39), and 5 μm (36, 37).