Figure 3. Kinetic Modeling of Cholesterol Efflux From Tissues In Vivo by Isotope Dilution.
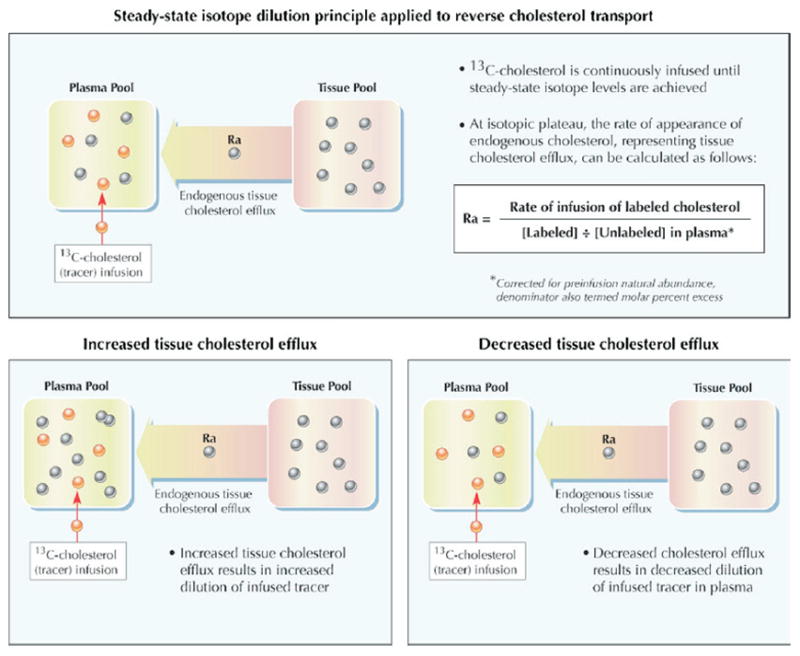
The flow of cholesterol from tissue to plasma, which encompasses the first step in RCT, can be assessed in vivo by noting the dilution of exogenous labeled cholesterol infused directly into the plasma compartment until steady-state levels are attained (47,48). The tracer abundance in plasma is diluted by the efflux of endogenous (unlabeled) cholesterol from tissues into plasma. At the isotopic plateau, the rate of appearance of endogenous cholesterol, representing tissue cholesterol efflux, equals the rate of tracer infusion divided by the plasma molar percent enrichment with labeled cholesterol. Figure illustrations by Rob Flewell. Abbreviations as in Figure 1.
