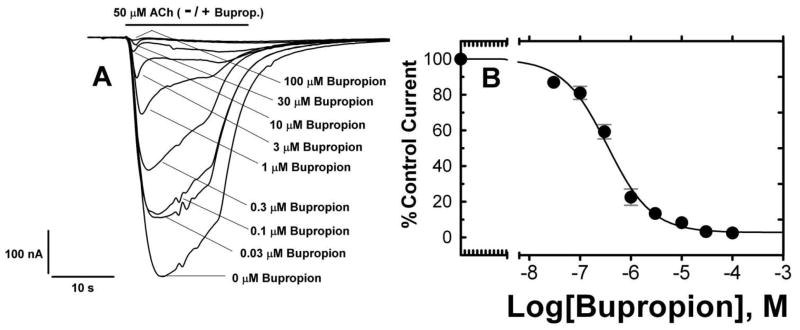
Figure 2. Bupropion Inhibition of ACh-evoked currents of Torpedo AChRs microinjected into Xenopus oocytes.
Currents elicited by ACh from affinity-purified and lipid-reconstituted (DOPC/DOPA/CH 3:1:1) Torpedo nAChR vesicles microinjected into Xenopus oocytes were measured using a standard two-electrode voltage clamp at a holding potential of −60 mV. (A) Once a stable response was observed for an EC50 dose (50 μM) of ACh, responses were measured when ACh was applied simultaneously for 20 seconds with increasing concentrations of bupropion (0.03–100 μM), and in each case a representative current trace is displayed. Inhibition by bupropion was reversible since peak responses to ACh returned to control levels after exposure to 3 μM bupropion followed by a six minute wash (not shown). (B) Nonlinear least-squares analysis of the curves yielded an IC50 = 0.34 ± 0.07 μM, nH = 0.98 ± 0.14 (7 oocytes). Currents were normalized to the 50 μM ACh response.