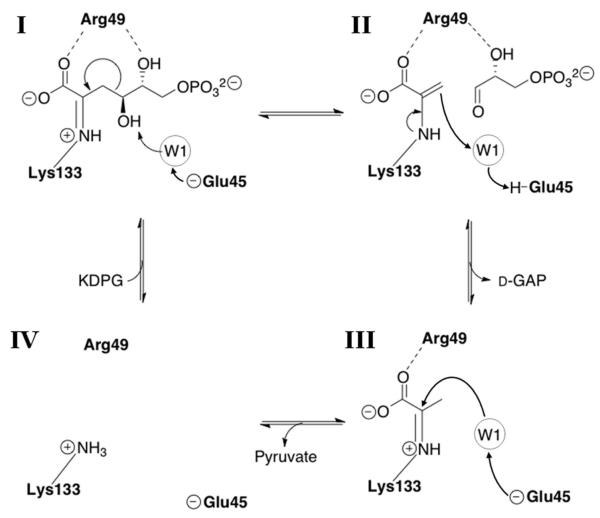
Scheme 1.
Catalytic mechanism of E. coli KDPG aldolase.(29, 30) The substrate is bound as a Schiff base adduct with Lys133 (I) and water W1 arises from the keto-group that is displaced by Schiff base formation.(30) Glu45 catalyzes proton removal from the C4 hydroxyl of KDPG. This proton transfer is mediated by W1. The C3-C4 bond is broken with the Schiff base stabilizing the formation of a carbanion at C4 to form D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and a pyruvyl-enamine (II). The pyruvyl-enamine is protonated by the acidic form of Glu-45 via W1 to form a Schiff base (III). Finally, the pyruvyl-Schiff base is hydrolyzed resulting in the free enzyme (IV).