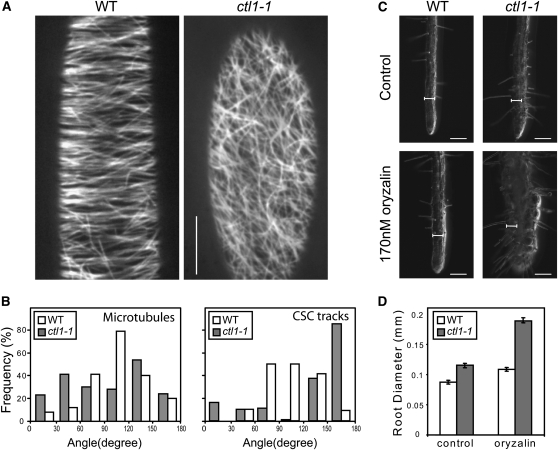
Figure 2.
Microtubule Defects in the ctl1-1 Mutant.
(A) Microtubule organization in wild-type (WT) and ctl1-1 etiolated hypocotyls visualized by confocal microscopy using the microtubule marker GFP:MAP4.
(B) Quantification of the orientation of microtubules and CSC tracks at the cell cortex and plasma membrane, respectively, of wild-type (white) and ctl1-1 (gray) etiolated hypocotyls. For microtubules, n = 200 in five cells from five seedlings; for CSCs, n = 160 in four cells from four seedlings. The plane perpendicular to the elongating direction is considered as reference (0° to 180°).
(C) and (D) ctl1-1 displays increased sensitivity to oryzalin.
(C) Root phenotypes of 5-d-old wild type and ctl1-1 grown on control- and 170 nM oryzalin-containing media.
(D) Measurement of root swelling in oryzalin-treated seedlings. Data represent the average (±se) of n = 50 seedlings.
Bars = 10 μm in (A), 100 μm in (C), and 66.5 μm for the internal scale.