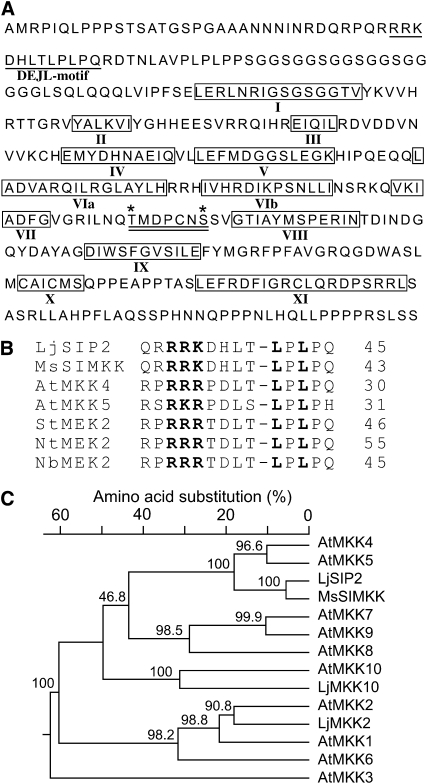
Figure 1.
SIP2 Is a MAPKK from L. japonicus.
(A) Deduced amino acid sequence of SIP2. The conserved DEJL motif is underlined. The catalytic subdomains I to XI of protein kinases are boxed and indicated by Roman numbers. Two putative phosphorylation sites of Thr and Ser are marked with asterisks. The activation loop, which comprises the two phosphorylation residues and is a putative target of upstream MAPKKKs, is underlined twice.
(B) The highly conserved DEJL motif of L. japonicus SIP2 and Arabidopsis MAPKKs. It has a consensus of K/R-K/R-K/R-X(1-5)-L/I-X-L/I and is designated for its putative role as the docking site for mammalian ERK and JNK MAPKs or LXL. The highly conserved Leu-X-Leu/Ile (LXL) motif provides a hydrophobic site for binding with MAPKs via hydrophobic interaction. The basic residues (RRK) within the DEJL motif interact with acidic residues of MAPKs via salt bridges. The last residue in each protein is indicated by a number.
(C) Phylogenetic tree of L. japonicus SIP2, MAPKK2, and MAPKK10, M. sativa SIMKK, and Arabidopsis MAPKK family members. SIP2 is most closely related to At-MKK4 and At-MKK5. Multiple sequence alignment and neighbor-joining phylogenetic analysis were performed using DNAStar software. Bootstrap values (%) obtained from 1000 trials are given at branch nodes. The alignment used to generate this tree is available as Supplemental Data Set 1 online.