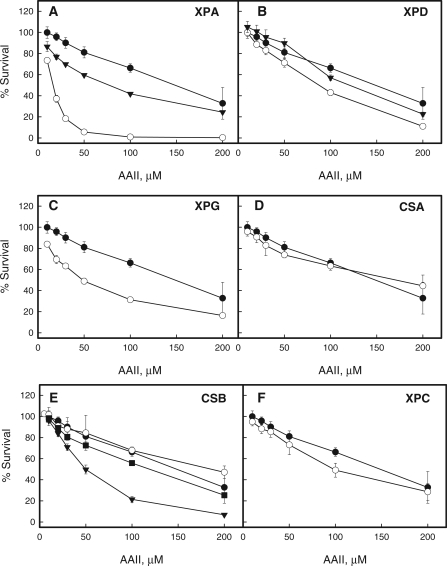
Figure 2.
AAII cytotoxicity study. (A–F) XP-, CS-deficient and control normal human fibroblasts cell lines were treated with 5–200 µM AAII for 72 h with the following ATP level measurements. Filled circles indicate the control normal human fibroblasts cell line, open circles—the deficient cell lines corresponding to the panel names, filled triangles—complemented cell lines if available. In the case of CSB-deficient cell lines, the complementation of the deficient cell line was achieved through pc3.1 plasmid vector harboring the cDNA of wild-type or ATPase mutant ERCC6 gene. On the F, filled squaresindicate the CSB-deficient cell line complemented with ATPase mutant gene. To correct the abnormal phenotype XPA-deficient cells are transfected with the full-length cDNA of the XPAC gene. The XPD cell line is transfected with p2E-ER2, a complementary DNA expression construct of the ERCC2 (XPD) gene, to correct the abnormal phenotype. The point for each AAII dose corresponds to the ATP ratio between treated and untreated cells and presents mean ± standard deviation for at least six measurements in two independent experiments.