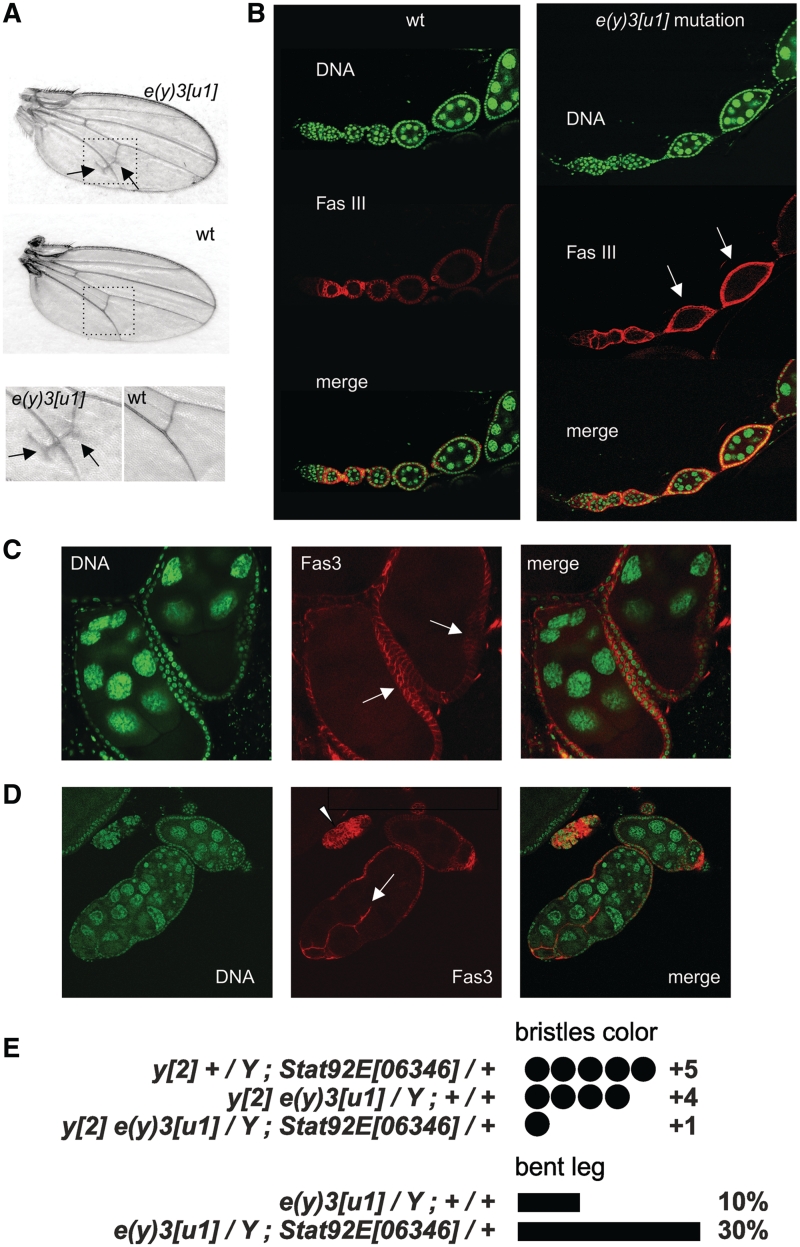
Figure 1.
Manifestations of e(y)3u1 mutation. (A) Wing venation abnormalities in mutants, compared to wild-type (wt) flies. Arrows indicate the ectopic longitudinal vein material close to the posterior cross-vein. The bottom row shows images of the posterior cross-vein region at higher magnification. (B) Ovarioles from wild-type and homozygous mutant flies. Fas3-positive cells in wt flies are detected until stage 2, whereas in mutants they could be found in follicles of stages 3–4 (arrows). Staining with DAPI (green), Fas3 (red), and merged images are shown. (C) Egg chambers with several layers of follicle cells (arrows). (D) Fused follicles with invasive follicular epithelium (arrow) and an island of overproliferated follicular cells (arrowhead). (E) The level of bristle coloring and the frequency of bent leg phenotype in flies carrying the e(y)3 and Stat92E mutations. A combination of both mutations aggravated the mutant phenotype.