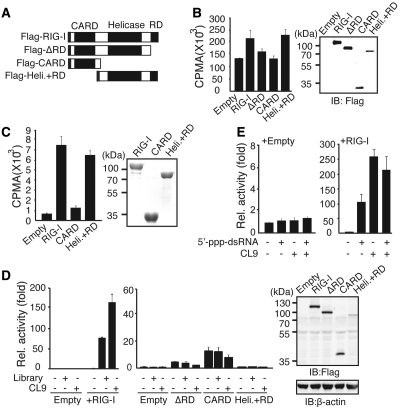
Figure 5.
CL9 binds to the RD-containing Helicase domain of RIG-I. (A) Schematic diagram of the RIG-I mutants used in this study. (B) Left, AP-treated 32P-CL9 was mixed with the indicated proteins that were over-expressed in HEK293 cells. Right, The expression level of the transfected protein was measured by western blot assay. (C) Left, Wild-type or mutant forms of RIG-I protein were purified from bacteria and incubated with AP-treated 32P-CL9 in vitro. Right, The expression of each protein was measured by Coomassie blue staining (D) Left, Huh7 cells were transfected with various RIG-I mutant plasmids as indicated, along with PRD-III-I-Luc and pRL-CMV, and luciferase activity was assayed after stimulation for 6 h. Right, Ectopic expression of RIG-I mutants was measured using an anti-Flag antibody. (E) Similar to (D), except cells were stimulated with 5′-triphosphate-dsRNA (100 pmol) and/or AP-treated CL9 (100 pmol) for 6 h. Data from more than three independent experiments, mean ± SD.