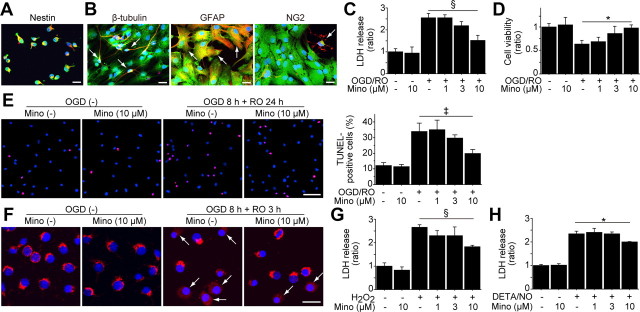
Figure 1.
Reduced NSC death with minocycline preconditioning in vitro. A, The NSCs grown as adherent cultures were examined by immunocytochemistry for GFP (green) and the NSC marker nestin (red). Nearly all the GFP-positive cells colocalized with nestin (yellow). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 μm. B, After culturing in differentiation medium containing 1 μm retinoic acid and 1% fetal bovine serum for 5 d, GFP-positive cells (green) expressed the neuronal marker β-tubulin, the astrocytic marker GFAP, and the oligodendrocytic marker NG2 (red) (arrows). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 20 μm. C, LDH assay demonstrated a significant reduction in NSC death with minocycline preconditioning (10 μm) after 8 h of OGD and 24 h of reoxygenation (n = 4). Mino, Minocycline; RO, reoxygenation. D, WST-1 assay showed significantly increased cell viability with 10 μm minocycline after 8 h of OGD and 24 h of reoxygenation (n = 4). E, NSCs analyzed by TUNEL staining (red) and DAPI (blue) after 8 h of OGD and 24 h of reoxygenation. Scale bar, 50 μm. The cell-counting study revealed a significant decrease in TUNEL-positive cells with minocycline preconditioning (10 μm) (n = 4). F, Fluorescent staining of cytochrome c (red) and DAPI (blue) after 8 h of OGD and 3 h of reoxygenation. The NSCs in which cytochrome c was released from mitochondria to the cytoplasm are indicated by arrows. Scale bar, 20 μm. G, H, Preconditioning with 10 μm minocycline significantly reduced the release of LDH from the NSCs under the oxidative stimuli of 200 μm H2O2 (G) and 250 μm diethylenetriamine/nitric oxide (DETA/NO) (H) (n = 4). *p < 0.05; ‡p < 0.005; §p < 0.001.