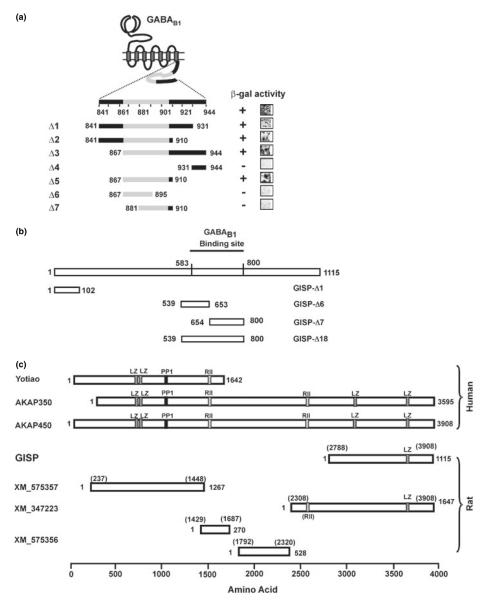
Fig. 1.
Isolation of GISP and characterization of binding domains. (a) Identification of GISP binding domain on GABAB1. Grey region denotes the coil-coiled domain. Truncation mutagenesis of GABAB1 defined residues Glu867–His910 as the minimal region required for GISP binding. Representative b-galactosidase stain of yeast colonies is illustrated. (b) Schematic diagram showing the truncated mutants of GISP used in this study. When used in the yeast two-hybrid assay, only Δ18 (539–800) and the original cDNA fragment from the screening activated the β-galactosidase reporter. (c) Comparison of GISP with other AKAPs transcribed from the same gene akap9. Human yotiao, AKAP350 and AKAP450 have been characterized at the protein level. With the exception of GISP, the rat proteins are hypothetical from expressed sequence tag (EST) sequences. LZ, leucine zipper domain; PP1, protein phosphatase 1 consensus binding motif, RII, PKA RII consensus binding motif.