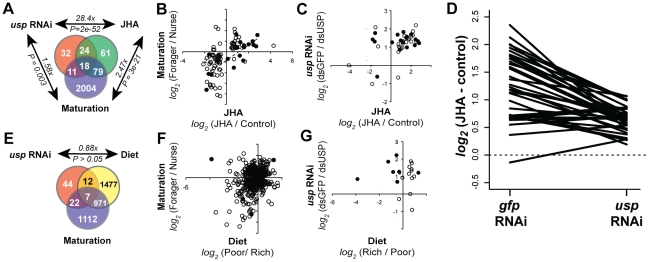
Figure 3. USP mediates maturation-related gene expression responses to juvenile hormone.
Mechanisms linking USP's putative targets to maturation were examined by studying their expression dynamics during maturation and in response to juvenile hormone analog treatments (JHA) and diet manipulations. A. usp RNAi, JHA, and maturation influence many of the same genes. Fold enrichment of overlap between gene lists and its hypergeometric p-value are indicated for each comparison. B. Fold change responses to JHA and maturation are positively correlated. Data are shown for 97 genes that responded significantly to both JHA and maturation; genes that also responded to usp RNAi are represented by closed circles. C. 33 of the 42 genes that respond to both JHA and usp RNAi were activated by both factors. Genes that also responded to maturation are represented by closed circles. D. usp RNAi inhibited transcriptional responses to JHA. Fold responses to JHA in control (gfp RNAi) and usp RNAi conditions are shown for each of the 33 genes that were activated by both USP and JHA. E. Few usp RNAi-responsive genes are regulated by diet quality. F. Fold change responses to diet quality and maturation are weakly correlated (978 genes that responded significantly to both). G. Fold change responses to usp RNAi and diet quality are uncorrelated (19 genes that responded significantly to both; genes that also responded to maturation are represented by closed circles).