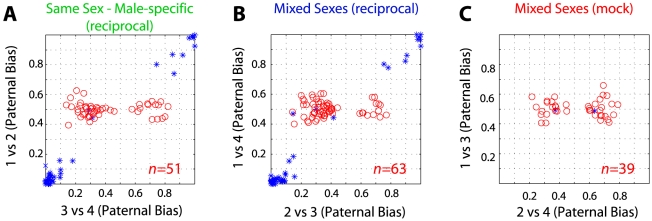
Figure 4. False-discoveries explain the majority of sex-specific imprinted genes.
Frequency of SNPs meeting the criteria used in [16], [17] to report sex-specific imprinted genes when comparing male PFCs from reciprocal crosses (A) as in [16], [17] as well as mixed-sex reciprocal (B) and mixed-sex mock comparisons (C). Red points (o) are SNPs that are biased toward the same parent-of-origin (exceed 10 read counts, p<0.05) in the comparison indicated on the x-axis but not in the comparison indicated on the y-axis (the criteria in [16], [17] for sex-specific imprinted gene calls). Blue points are SNPs exceeding significance in comparison of animals on both axes.