Table 2. Power-law fitting results for Bark-band code-words per database and window size.
| DB/Window | N words |
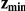
|
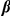
|

|
| Speech | ||||
| 46 ms | 494,926 | 2,000 | 2.20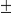 .05 .05 |
0.84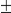 .04 .04 |
| 186 ms | 219,595 | 501 | 2.22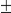 .05 .05 |
0.82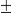 .03 .03 |
| 1,000 ms | 100,273 | 79 | 2.33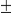 .05 .05 |
0.75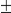 .03 .03 |
| Music-W | ||||
| 46 ms | 1,724,245 | 2,000 | 2.26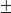 .04 .04 |
0.79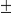 .03 .03 |
| 186 ms | 798,871 | 794 | 2.33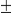 .06 .06 |
0.75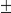 .03 .03 |
| 1,000 ms | 240,236 | 79 | 2.29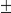 .03 .03 |
0.78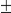 .02 .02 |
| Music-nW | ||||
| 46 ms | 1,905,444 | 126 | 2.17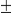 .01 .01 |
0.85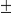 .01 .01 |
| 186 ms | 947,327 | 50 | 2.17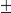 .01 .01 |
0.85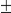 .01 .01 |
| 1,000 ms | 306,682 | 5 | 2.17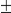 .01 .01 |
0.86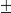 .01 .01 |
| Elements | ||||
| 46 ms | 125,248 | 794 | 1.95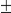 .04 .04 |
1.05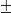 .05 .05 |
| 186 ms | 34,171 | 20 | 1.79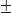 .02 .02 |
1.27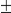 .03 .03 |
| 1,000 ms | 10,231 | 8 | 1.79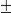 .02 .02 |
1.27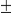 .03 .03 |
DB/Window means database name and window size, N words is the number of used code-words, 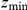 is the minimum frequency for which the Zipf's law is valid,
is the minimum frequency for which the Zipf's law is valid, 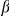 is the frequency-distribution exponent (Eq. 2), and
is the frequency-distribution exponent (Eq. 2), and  corresponds to the Zipf's exponent (Eq. 1).
corresponds to the Zipf's exponent (Eq. 1).
