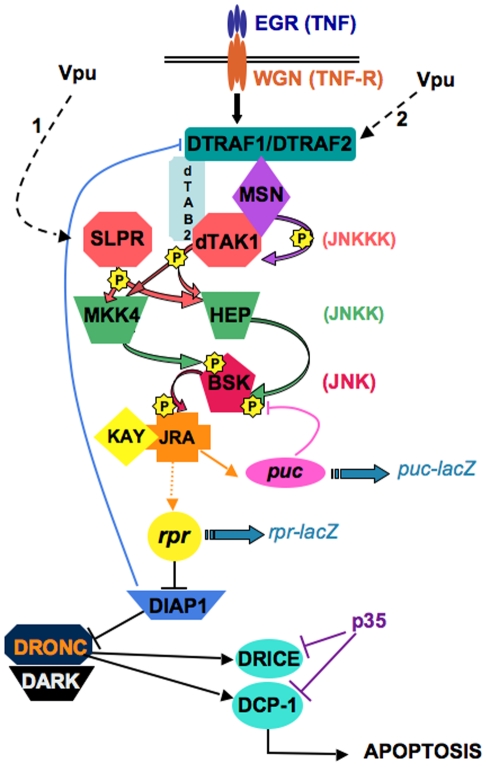
Figure 9. Model: Vpu activates the JNK pathway upstream of JNKKKs.
The JNK pathway is a kinase cascade that, when activated in Drosophila, leads to phosphorylation of the transcription factors JRA (Jun-related antigen) and KAY (Kayak). puckered (puc) is a transcriptional target of the JNK pathway and acts in a negative feedback loop to dampen JNK signaling. The activation of this cascade also leads to the transcriptional activation of the pro-apoptotic gene rpr that in turns leads to the degradation of the anti-apoptotic factor DIAP1, which activates caspases such as DRONC/Caspase 9 and its specific co-factor DARK/Apaf-1, DRICE/Caspase 3 and Death Caspase-1 (DCP-1) resulting in the onset of apoptosis. Although reaper does not have a direct human homolog, mammalian Smac/DIABLO was shown to be a functional homolog of Reaper/Hid/Grim, that acts by reducing c-IAP protein levels through the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway [92]. Two JNKKs, HEP and MKK4, phorphorylate the JNK/BSK at different sites. These are phosphorylated by several Drosophila JNKKKs, among which SLPR and dTAK1, the latter being a target for phosphorylation by MSN. DTRAF1 and DTRAF2 are intracellular proteins known to activate JNKKKs. TAK1-associated binding protein 2 (dTAB2) is an adaptator protein linking dTRAF1 to dTAK1. The ligand-receptor interaction between EGR/WGN (TNF/TNFR) has been shown to induce JNK pathway-mediated apoptosis. Yellow stars: phosphorylation activity of the kinases. Blue, pink and violet lines: negative regulators (DIAP1 overexpression, and PUC and P35 expression negatively regulate DTRAF1, BSK and effector caspase activities, respectively). Wide blue arrows: lacZ reporter transgenes. The dotted arrows 1 and 2 indicate the candidate targets of Vpu suggested by this work.