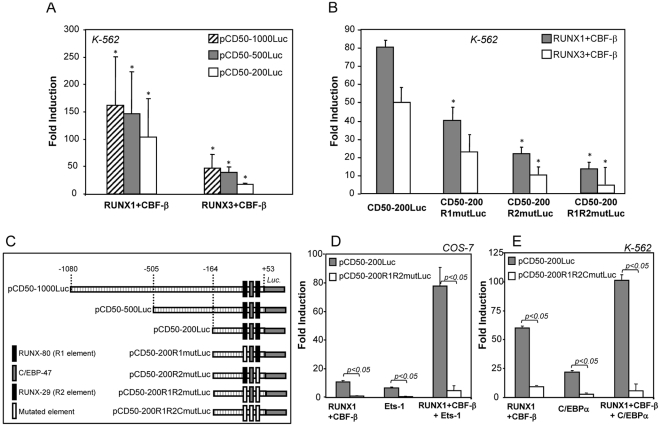
Figure 3. RUNX factors regulate the activity of the ICAM-3 promoter through the recognition of both RUNX-binding sites.
A. K-562 cells were transfected with 1 µg of the indicated reporter plasmid in the presence of CMV-0 (empty expression vector), pCMV-RUNX1 or pCDNA3-RUNX3, and luciferase activity determined after 24 h. For each individual reporter construct, fold induction represents the luciferase activity yielded by an expression vector relative to the activity produced by a similar amount of CMV-0 plasmid. Data represent mean ± SD of 4 independent experiments using distinct DNA preparations. (*P<0.005 compared with the activity of pCMV-0–transfected cells). B. K-562 cells were transfected with 1 µg of the indicated reporter plasmids in the presence of CMV-0, RUNX1/CBF-β or RUNX3/CBF-β expression plasmids, and luciferase activity determined after 24 h. (*P<0.05 compared with the activity of pCD50-200Luc–in the presence of RUNX1/CBF-β or RUNX3/CBF-β, respectively). C. Schematic representation of the proximal regulatory region of the ICAM-3 gene and reporter plasmids used for its functional dissection. D. COS-7 cells were transfected with the indicated reporter plasmids in the presence of CMV-0, RUNX1/CBF-β or Ets-1 expression plasmids, and luciferase activity determined after 24 h. E. K-562 cells were transfected with 1 µg of the indicated reporter plasmids in the presence of CMV-0, RUNX1/CBF-β or C/EBPα42 expression plasmids, and luciferase activity determined after 24 h. In B, D, E, for each individual reporter construct, fold induction represents the luciferase activity yielded by an expression vector relative to the activity produced by a similar amount of CMV-0 plasmid. Data represent mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments.