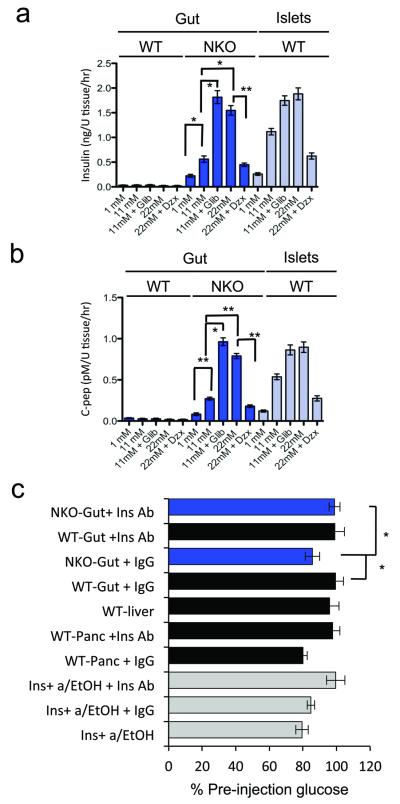
Figure 3.
Insulin secretion and bioactivity. (a, b) Glucose-dependent insulin and C-peptide secretion from NKO (blue bars) and control gut or islets (gray bars) of adult mice incubated with the indicated concentrations of glucose and 0.5 mM diazoxide (Dzx), or 10 nM Glibenclamide (Glib) (n = 4). U tissue corresponds to 1-inch of gut or one islet. (c) Effects of acid-ethanol extracts from NKO (blue bars) or control mice (gray bars) on glucose levels following subcutaneous injections in 5-day-old mice. Samples were pre-incubated with anti-insulin neutralizing antibody (Ins Ab), or isotype-matched control IgG (IgG). Recombinant human insulin (2U per kg body weight) was subjected to acid-ethanol precipitation prior to injection (acid/EtOH) (n = 8 in a-b, and n = 12 in c). 3 independent experiments were performed for secretion assays and 2 for bioassay. * = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.01. Error bars indicate SEM.