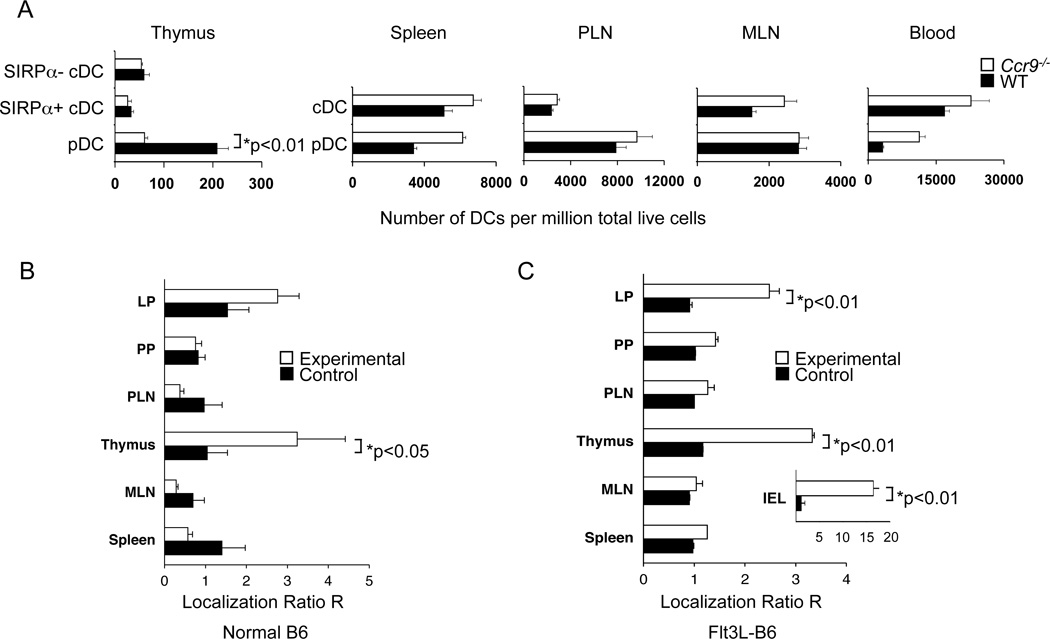
Figure 1. CCR9 controls pDC representation in the thymus under competitive and non-competitive conditions.
A. Blood leukocytes and cell suspensions from thymi, spleen, peripheral lymph nodes (PLN) and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) from untreated C57BL/6 (WT) and Ccr9−/− mice were analyzed by flow cytometry for the number of lineage (lin) (CD3, CD19, NK1.1)neg pDCs (CD11cint B220+ PDCA-1+) and cDCs (CD11chi B220− PDCA-1−) as well as thymic SIRPα+ (CD11b+) and SIRPα− (CD11b−) cDCs. Bar graphs present the mean number of DCs per million live cells (±SEM; 5 mice per group) from one of two experiments. B, C. Bone marrow chimeras (BMC) were generated by reconstituting lethally irradiated WT F1 (CD45.1 × CD45.2) mice with equal numbers of “experimental” Ccr9−/− (CD45.2) bone marrow (BM) cells mixed with congenic WT (CD45.1) BM cells (white bars) or “control” WT (CD45.2) BM cells mixed with congenic WT (CD45.1) BM cells (black bars). Tissues were harvested 8–12 weeks later and cell suspensions analyzed by flow cytometry. To assess BM engraftment efficiency of each donor type, the CD45.1/CD45.2 ratio for BM-derived splenic CD19+ B cells was determined. For each mouse, the CD45.1/CD45.2 ratio among gated (Lin- CD11cint, B220+) pDCs in each tissue was normalized for the engraftment efficiency to yield normalized localization ratios (R): R= (CD45.1/CD45.2)Tissue pDCs/(CD45.1/CD45.2)Splenic B cells. Reconstituted chimeric mice in the left panel (B) were evaluated without further treatment, whereas the pDCs in BMCs in the right panel (C) were expanded by inoculation of mice with Flt3L-secreting B16 tumors. Overall, results are representative of 3 experiments with 4–5 BMC pairs analyzed. See also Figure S1.