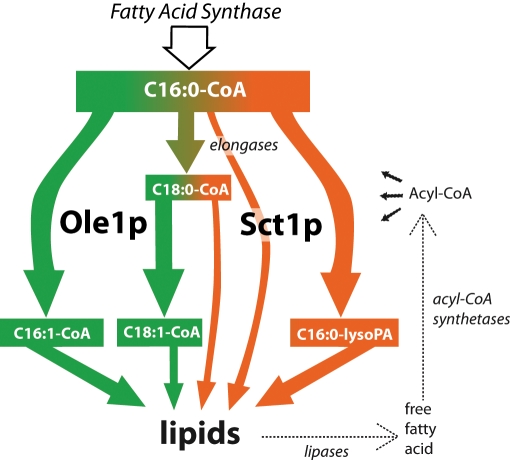
FIGURE 7:
Proposed mechanism for regulation of fatty acid desaturation by competition for C16:0-CoA between Sct1p and Ole1p. C16:0-CoA synthesized by the fatty acid synthase is sequestered into lipids by Sct1p and possibly other acyltransferases, decreasing desaturation (orange). Alternatively, Ole1p introduces a double bond, yielding C16:1-CoA and increasing desaturation (green). The elongases produce C18:0-CoA, which can be incorporated into lipids by Sct1p or other acyltransferases or converted into C18:1-CoA by Ole1p. Free fatty acids originating from lipid degradation by lipases recycle into the acyl-CoA pool after activation by acyl-CoA synthetases. To reduce complexity, elongation of acyl-CoA beyond C18 and metabolic fates of acyl-CoA's other than incorporation into lipids are omitted in the diagram.