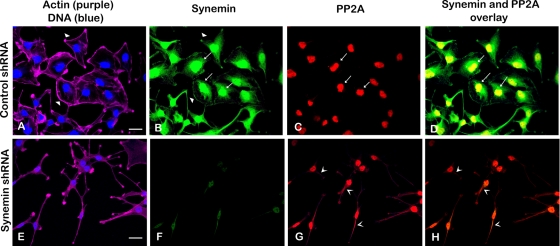
FIGURE 7:
Fluorescence staining of A172 cells treated with control (A–D) or synemin (E–H) shRNAs. Staining was performed with four fluorescent reagents: phalloidin Alexa 633 (to stain actin; purple) and DAPI (to stain DNA; blue; A, E), Alexa 488 synemin antibodies (green; B, F), and Alexa 568 PP2A antibodies (red; C, G). (A, E) Actin staining shows that control cells are polygonal in shape with prominent peripheral actin (A, arrowheads), whereas synemin-silenced cells have an elongated cell body with cytoplasmic processes (E). (B, F) Staining with synemin antibodies shows that in control cells synemin is localized at the cellular periphery (B, arrowheads), as well as in the nuclear area (B, arrows); synemin staining is decreased after synemin silencing (F). (C, G) Staining with PP2A antibodies shows that PP2A is present in the nuclear area of control cells (C, arrows); after synemin silencing, PP2A antibodies stain the cytoplasm as well (G, V-shaped arrowheads). (D, H) Overlay of synemin and PP2A staining appears yellow and reveals that the two proteins overlap in the nuclear area of control cells (D, arrows); little overlap is seen in synemin-silenced cells (H). Bars, 10 μm.