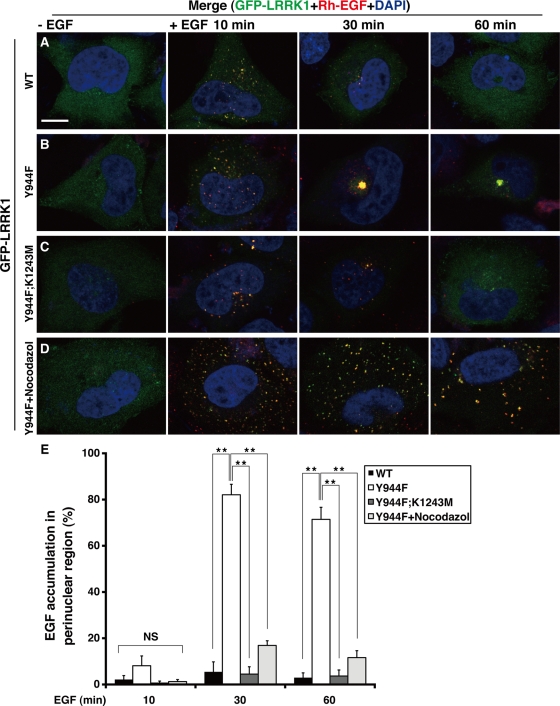
FIGURE 4:
LRRK1(Y944F) leads to EGF accumulation in endosomal compartments in the perinuclear region. (A–D) Distribution of Rh-EGF. HeLa S3 cells were transfected with wild-type GFP-LRRK1 (A), GFP-LRRK1(Y944F) (B, D), and GFP-LRRK1(Y944F; K1243M) (C), as indicated. After 16 h of serum starvation, cells were briefly stimulated with or without Rh-EGF (40 ng/ml), followed by washing to remove labeled EGF from the medium. The cells shown in D were preincubated with nocodazole (5 μg/ml) for 30 min before EGF stimulation. Cells were incubated for the indicated times after the initial exposure to Rh-EGF and then fixed and stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Yellow colors in the merged images indicate colocalization of GFP-LRRK1 and Rh-EGF. Scale bar, 10 μm. (E) Quantification of the EGF accumulation in the perinuclear region. Histogram indicates the percentage of cells that have endosomes (>2.0 μm diameter) containing Rh-EGF in the perinuclear region. Values reflect the mean SD of three independent experiments, with an average of 50 cells scored per samples. Data are compared using a two-tailed unpaired Student's t test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; NS, not significant.