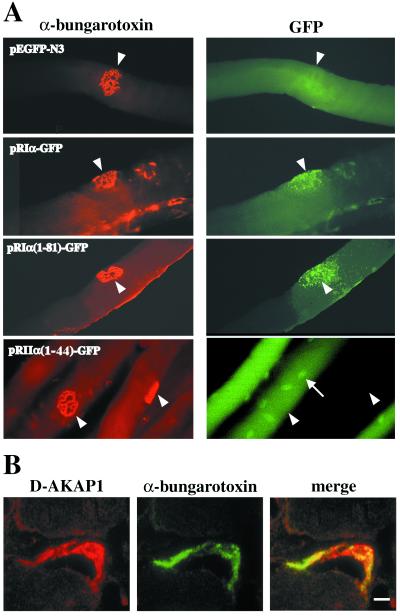
Figure 4.
Accumulation of RIα-GFP fusion proteins and of D-AKAP1 at the NMJ. (A) The dimerization domain of RIα, but not of RIIα, is able to direct NMJ localization. Plasmids encoding full-length or truncated RIα-GFP or RIIα(1–44)-GFP fusion proteins were injected into tibialis anterior muscles. Whole fibers expressing GFP were dissected and stained with tetramethylrhodamine B isothiocyanate-α-bungarotoxin to reveal the NMJ (open arrowheads). A fiber negative for GFP is shown in Lower Right. The arrow points to a nucleus in the multinucleated muscle fiber. (B) Confocal microscopy images of an adult muscle NMJ double-stained with anti-D-AKAP1 antibody and FITC-α-bungarotoxin. The photos show a single optical slice. (Bar = 5 μm.)