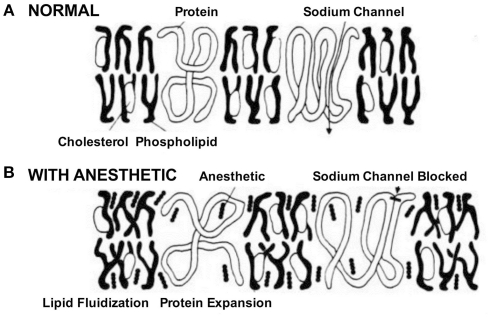
Figure 1.
Schematic of the effects of anesthetics on cell membrane and Na+ channels. In the absence of the drug. (A) Na+ channels initiate and propagate electrical signals, i.e., action potentials. (B) The anesthetic was believed to affect Na+ channels by partitioning and interacting with the membrane. This process called lipid fluidification altered the cell membrane and subsequently distorted the channel protein leading to block of channel function (Seeman, 1974).