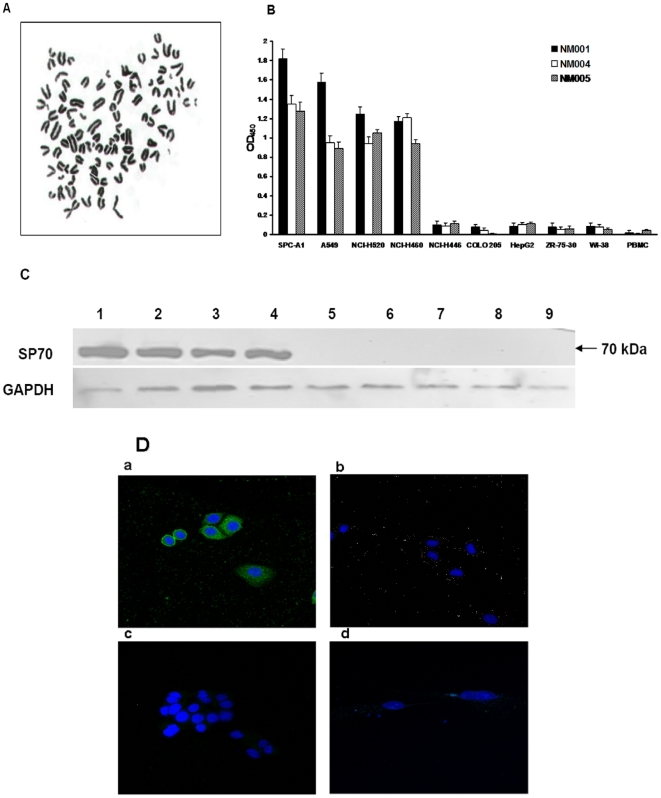
Figure 1. Production and characterization of NJ001.
(A) Karyotype of NM001 hybridoma cell line (×400). (B) Binding activity of McAbs to human maligant and nonmaligant cells in culture. Undiluted supernatants from hybridomas NM001, NM004, NM005 were tested in triplicate with indirect cell ELISA as described in “Materials and Methods”. Each number represents the average absorbance of the substrate end product at 450 nm. Controls without McAbs exhibited an average absorbance of 0.02. NM001 was selected for further study as it exhibited the greatest binding ratio with lung tumor cells and the greatest specificity for the lung cancer cell lines compared with the other tumor cell lines. (C) Western blot analysis for the reaction of NJ001 produced from hybridoma NM001 with different cells (human maligant and nonmaligant cells) in culture. (Lane 1, SPC-A1; lane 2, A549; lane 3, NCI-H520; lane 4, NCI-H460; lane 5, HepG2; lane 6, ZR-75-30; lane 7, COLO 205; lane 8, WI-38; lane 9, PBMC; lane 10, Marker). GAPDH was used as a loading control. Results indicated that the expression of protein was specific to antibody NJ001 in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines, not in other cancer cell lines and normal cells. (D) Representative positive and negative results obtained from IIF analysis of reaction of NJ001 with different cells observed by fluorescence and confocal microscopy analysis (×400). (a, SPC-A1; b, ZR-75-30; c, HepG2; d, WI-38). Presence of NJ001 can be visualized in cellular cytoplasm of SPC-A1 cells, but other cell lines showed no fluorescence. Localization of the antigen specific to NJ001 may be in cellular cytoplasm of SPC-A1 cells.