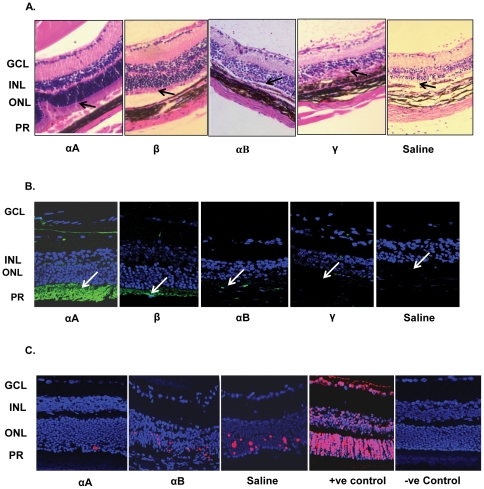
Figure 2. Intravenous administration of αA protects retinal photoreceptors.
Twelve days after EAU was induced in B10RIII (WT) mice with an IRBP peptide, the animals were injected with various crystallins and the retinas were collected and examined on day 21. A, B and C: αA = αA crystallin, β = β crystallin, αB = αB crystallin, γ = γ crystallin and saline. A. Histology of retina and uvea (Hematoxylin and Eosin stained). Arrows indicate photoreceptor inner segments (PR). Note presence of photoreceptors in αA and their degeneration (absence) in Saline treated animals. B. Retinal architecture as revealed by immunostaining for IRBP with anti-IRBP (green, arrows). C. Apoptosis in EAU retinas of animals treated with various crystallins; αA treated, αB treated, saline treated, positive (+ve) control (DNase I treated retina) and (‘no enzyme’) negative (−ve) control. Note that retinal photoreceptors are preserved (A, αA and B, αA); there is little or no apoptosis (TUNEL positive cells) in αA treated animals (C, αA). PR = Photoreceptors, ONL = Outer nuclear layer, INL = Inner nuclear layer, GCL = Ganglion cell layer.