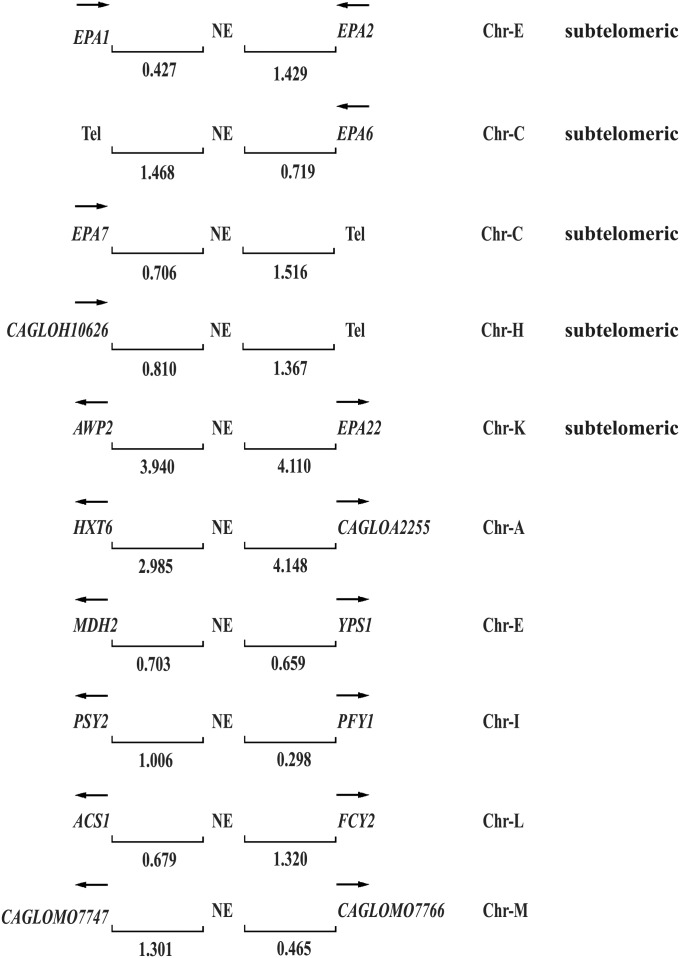
Figure 5 .
Blast analysis of the NE in the C. glabrata genome. The last 60 bp of the NE is associated with other EPAs and non-EPA genes. EPA1, EPA2, EPA6, EPA7, AWP2, and CAGLOH10626 (15) encode cell wall proteins, all are subtelomeric and the NE associated is localized at their 3′ ends, except for AWP2 and EPA22, which is localized between these two divergently transcribed genes. The NE associated to non-EPA genes is located at the 5′ regions (promoters) of these divergently expressed genes. HXT6 (high-affinity glucose transporter of the major facilitator superfamily), MDH2 (cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase), YPS1 (GPI-anchored aspartyl protease), PSY2 (putative subunit of an evolutionarily conserved protein phosphatase complex containing the catalytic subunit Pph3p and the regulatory subunit Psy4p), PFY1 (profilin, binds actin involved in cytoskeleton organization), ACS1 (acetyl-coA synthetase isoform), FCY2 (purine-cytosine permease), and CAGLOA2255, CAGL0M07747, and CAGL0M07766 are of unknown function (Saccharomyces Genome Database http://www.yeastgenome.org/ and C. glabrata Genome Database http://www.genolevures.org/cagl.html). Arrows indicate direction of transcription; numbers show the distance in kilobases between the negative element (NE) and the genes or the telomere (Tel); and Chr-(letter) denotes chromosome notation.