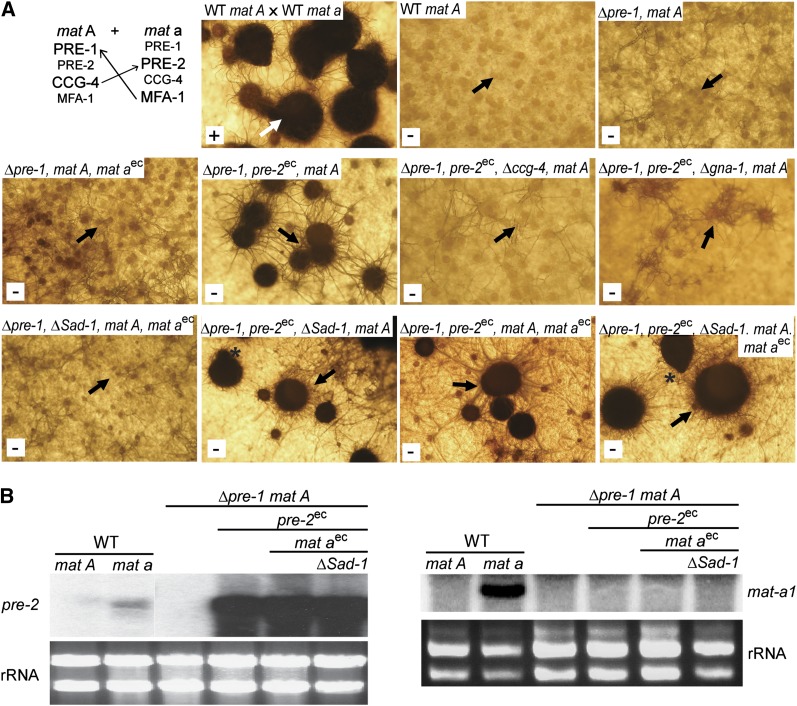
Figure 6 .
Perithecial development in the absence of opposite mating-type males. (A, top left) Cross of wild-type strains 74A and 74a (positive control for normal perithecial development). Protoperithecia from 6-day-old SCM cultures of strain 74A were fertilized with 74a and resulting perithecia were photographed 4 days later. The white arrow indicates an example of a normal perithecium. For all other panels, SCM plate cultures were grown for 10 days without fertilization. Strains are wild-type 74A (WT mat A), 16A (Δpre-1, mat A), P1A68 (Δpre-1, mat A, mat aec), P1A46 (Δpre-1, pre-2ec, mat A), P1C4A46 (Δpre-1, Δccg-4, pre-2ec, mat A), P1Gα1A46 (Δpre-1, pre-2ec, Δgna-1, mat A), P1A46-68-Sad1 (Δpre-1, ΔSad-1, mat aec, mat A), P1A46-Sad1 (Δpre-1, pre-2ec, ΔSad-1, mat A), P1A46-68 (Δpre-1, pre-2ec, mat aec, mat A), and P1A46-68-Sad1 (Δpre-1, pre-2ec, ΔSad-1, mat aec, mat A). The white box in the lower left corner of each panel indicates whether the strain produced ascospores (+ or −). Black arrows point to examples of protoperithecia or barren perithecia (enlarged bodies) developing in unfertilized cultures. The asterisks indicate beak formation in self-stimulated perithecia from the P1A46-68–Sad1 strain. Note that pre-2ec is Pccg-1::pre-2-FLAG::his-3+, while mat aec is mat a::bar. (B) Expression of pre-2 and mat a in self-stimulating strains. Total RNA was isolated from 6-day-old SCM plate cultures of wild-type mat A (74A), wild-type mat a (74a), Δpre-1, mat A (16A), Δpre-1, pre-2ec, mat A (P1A46), Δpre-1, pre-2ec, mat A, mat aec (P1A46-68), and Δpre-1, pre-2ec, mat A, mat aec, ΔSad-1 (P1A46-68-Sad1). Note that pre-2ec is Pccg-1::pre-2-FLAG::his-3+, while mat aec is mat a::bar. Samples containing 30 μg of total RNA were used to prepare Northern blots that were probed with pre-2 (left) and mat a (right). rRNA is used as a loading control.