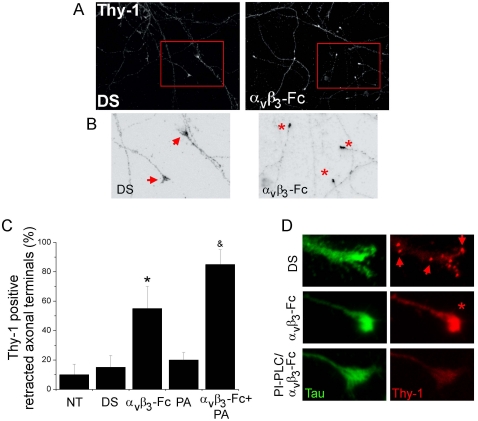
Figure 6. Collapse of axonal terminals of cortical neurons induced by recombinant αVβ3-Fc.
(A, B) Differentiated cortical neurons, 12–15 days in culture in vitro, were treated with supernatants containing αVβ3-Fc fusion protein (αVβ3-Fc) or with αVβ3-Fc-depleted supernatants (DS), supplemented or not with Protein A. Then, neurons were fixed and immunostained for Thy-1 (A–D) and Tau protein (D) and photographed using conventional fluorescence microscopy. (B) Digital zoom was applied to marked areas (red squares in A) and indicated areas were inverted by gray-tone scaling using ImageJ. (C) Quantification of Thy-1-positive retracted axonal terminals in neurons for each condition is plotted as a percentage of total cells. NT, non-treated neurons; DS, αVβ3-Fc-depleted supernatants; αVβ3-Fc, αVβ3-Fc-containing supernatant; PA, Protein A; αVβ3-Fc+PA, αVβ3-Fc-containing supernatant supplemented with Protein A (see Methods). Graphs show means+s.e.m. from at least 25 neurons per condition, n = 4. *, &, P<0.05 compared to their respective control. (D) Representative axonal terminals are shown from neurons treated with αVβ3-Fc-depleted supernatants (DS); αVβ3-Fc-containing supernatant (αVβ3-Fc); or 1 U/ml of PI-PLC added prior addition of αVβ3-Fc-containing supernatants (PI-PLC/αVβ3-Fc). Arrows point to Thy-1 clusters in axon and growth cone. Asterisk indicates a retracted axonal terminal.