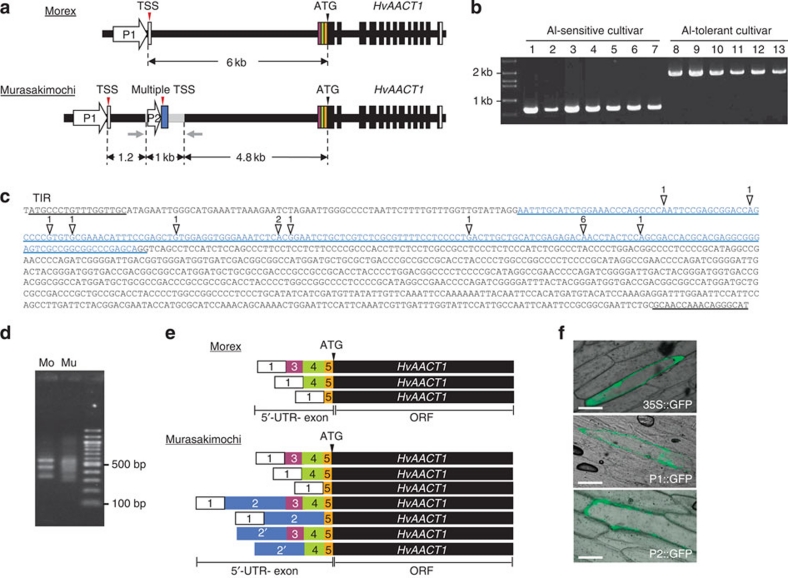
Figure 1. Location and function of the upstream insertion.
(a) Schematic presentation of the genomic structure of HvAACT1 in an Al-sensitive cultivar (Morex; Mo) and an Al-tolerant cultivar (Murasakimochi; Mu). White and colour vertical boxes show UTR exons. Black vertical boxes and black lines show ORF-exons and introns, respectively. Grey line shows a 1,023-bp insertion at the 4.8 kb upstream of the coding region in Murasakimochi. TSS, transcriptional start site. Grey arrows indicate the positions of PCR primers used for the insertion detection in b. (b) Detection of the 1-kb upstream insertion in different barley cultivars. 1, Morex; 2, Golden Promise; 3, BC95; 4, Z504; 5, K0046; 6, BC282; 7, BC366; 8, ALP3; 9, BC26; 10, Murasakimochi; 11, BC262; 12, BC191; 13, Akashinriki. (c) Sequence of HvAACT1 upstream insertion. White triangles show multiple HvAACT1 TSS and the number means frequency of identification of TSS by cloning. Sequence of blue character indicates 5′-UTR-2 in Murasakimochi. The insertion region contains a terminal inverted repeat (TIR) of 17 bp at the 5′ and 3′ ends. (d) Image of agarose gel showing the 5′-RACE PCR products. HvAACT1 gene-specific primer and RNA oligo primer were used for amplifying HvAACT1 5′-UTR region. (e) Schematic presentation of 5′-UTR variants of HvAACT1 between Morex and Murasakimochi. The sequences were read from 20 5′-RACE clones. White and colour boxes show the 5′-UTR and colours corresponding to diagram in a. The number in the box shows 5′-UTR position on the genome. Box 2′ includes variations from different transcriptional start sites. (f) Promoter assay. Common promoter (P1 in a), 1-kb insertion-originated region (P2 in a), or 35S promoter (as a control) was fused to GFP and then transiently introduced to onion epidermal cells. Scale bars, 100 μm.