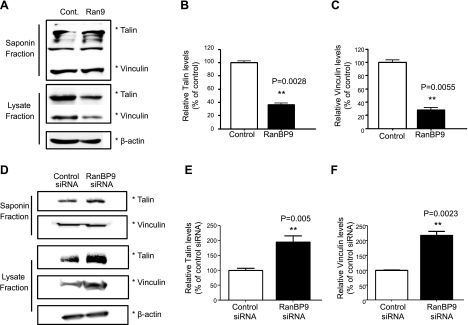
Figure 3.
RanBP9 inhibits focal adhesion assembly. A) NIH3T3 cells were transfected with either RanBP9 or empty vector for 48 h; cells were sequentially treated with saponin buffer on ice, saponin extractable material was collected, and remaining cells were extracted by SDS sample buffer and sonicated. Both saponin (nonfocal adhesion pool) and lysate fractions (focal adhesion enriched pool) were resolved on SDS-PAGE gel and subjected to immunoblotting for talin and vinculin. A representative experiment is shown. B, C) Quantitations from 3 experiments show that RanBP9 significantly reduces talin (B) and vinculin (C) in the lysate fraction without changes in the saponin fraction. Asterisks at right of immunoblots indicate protein band positions. D) NIH3T3 cells were transfected with control or RanBP9 siRNA twice over a 48-h period, and cells were subjected to cytosolic and focal adhesion fractionation, as above, followed by immunoblotting for talin and vinculin. Asterisks at right of immunoblots indicate protein band positions. On surface biotinylation and removal of surface biotin without internalization (SR0), no LRP or β1-integrin signals were detected. A representative experiment is shown. E, F) Quantitations from 3 experiments show that RanBP9 siRNA significantly increases talin (E) and vinculin (F) in the lysate fraction without changes in the saponin fraction. Asterisks at right of immunoblots indicate protein band positions. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.