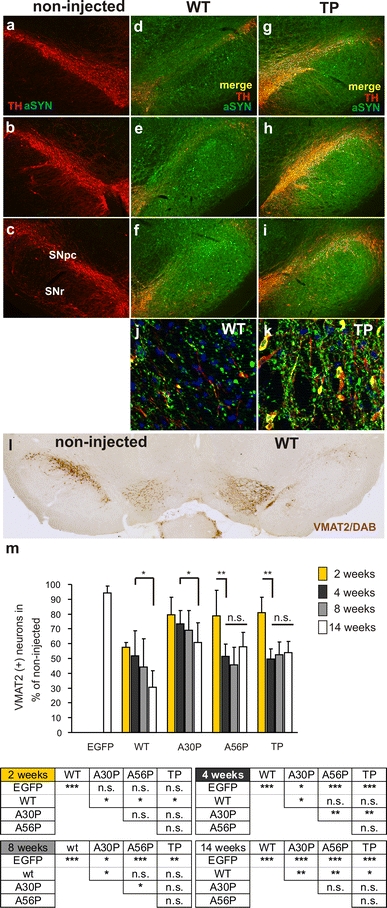
Only fibrillar αSynuclein variants induce progressive DA neuron degeneration in vivo.
a–
i Representative images illustrating nigral DA neurodegeneration and significant overexpression of αSynuclein in the injected hemispheres by double staining for TH (
red) and αSynuclein (
green). Each column contains rostral-to-caudal coronal sections taken from the same animal and gives an overview of the extent of nigral DA neuron loss induced by expression of WT (
d–
f) or TP (
g–
i) αSynuclein at 14 weeks after AAV injection. Non-transduced control sections are shown in
a–
c. Higher magnification images (
j,
k) are optical sections of 1 μm and were generated with an ApoTome. DA cell bodies which demonstrated immunoreactivity for both, the DA marker TH and human αSynuclein, were found more frequently for TP than for WT. (
l) Representative image of a coronal section showing nigral degeneration in a AAV-WT αSynuclein-injected animal. The nigral DA neurons were specifically labeled with an antibody against VMAT2 and with standard DAB immunohistochemistry. The expression of WT αSynuclein led to loss of VMAT2-positive neurons in the SNpc, compared with the contralateral intact side.
m Changes in total number of VMAT2-positive cells in SNpc over time, as determined by stereology in the AAV-αSynuclein-WT, A30P, A56P, TP and AAV-EGFP-injected rats (
n = 5–6 animals per time point and group). Data are shown as mean
±
SD; significant differences between groups outlined below the graph (Tukey’s test)