Figure 1.
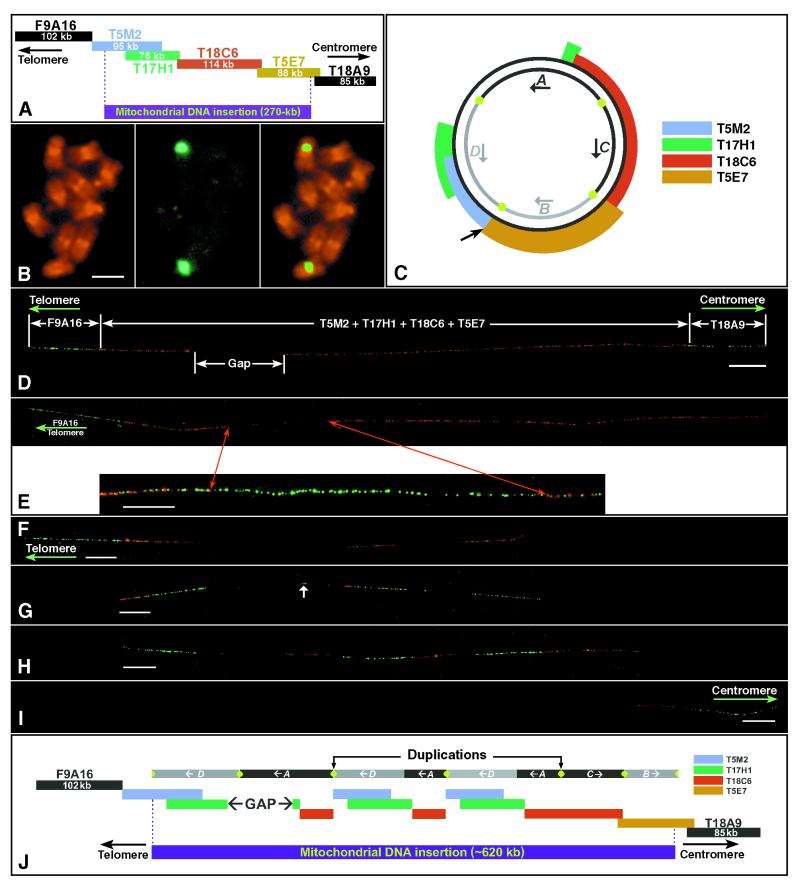
Cytological characterization of the mtDNA-insertion locus on chromosome 2 of A. thaliana. (A) The 491-kb contig of chromosome 2 sequenced by Lin et al. (6) consists of six BAC clones and includes two flanking nuclear BACs and four mtDNA-related BACs (see Results). Kilobase sizes are based on the sequencing data. (B) Hybridization of a mtDNA-related BAC T17H1 to the somatic metaphase chromosomes of A. thaliana (ecotype Columbia-0). (B Left) Propidium iodide-stained somatic metaphase chromosomes. (B Center) FISH signals detected by fluorescein isothiocyanate (green color). (B Right) A merged image of chromosomes and FISH signals. Hybridization signals were detected only in the pericentric regions on one pair of submetacentric chromosomes. (Bar = 2 μm.) (C) Homology of the four mtDNA-related BACs to the published C24 A. thaliana mitochondrial genome (11). Approximately 97 kb of the mtDNA genome is not present in the contig presented in A. The organization of the A, B, C, and D domains was originally proposed by Lin et al. (6) but is incorrectly represented in their figure 7 B and C. The green dots represent the two sets of specific repeats in the mitochondrial genome. The outside arrow points to the possible insertion point (see ref. 6). (D) Hybridization of the six BACs in A to DNA fibers of A. thaliana. The two nuclear flanking BACs are detected by FITC (green) and the four mtDNA-related BACs by rhodamine (red). The mtDNA-related BACs do not hybridize to a gap region. (Bar = 20 μm.) (E Upper) The gap region within the mtDNA insertion is localized to the telomere-proximal end by cohybridization of the telomere-flanking BAC clone F9A16 (green) with the four mtDNA-related BAC clones (red). (E Lower) Cohybridization of four mtDNA-related BACs (in red) with a set of 15 cosmid clones (in green), which comprise the complete mitochondrial genome of A. thaliana. The gap is filled by green signals derived from the cosmids, indicating that regions of the mitochondrial genome not included in the sequenced BAC contig are present within the mtDNA insertion locus on the chromosome. (Bar = 10 μm.) (F) DNA fiber hybridized with telomere-proximal BAC clone F9A16 (green) and mtDNA-derived BAC clone T5M2 (red). T5M2 shows a triplet pattern. (Bar = 20 μm.) (G) DNA fiber hybridized with the first mtDNA BAC T5M2 (red) and the second mtDNA BAC T17H1 (green). These two BACs, which share ≈54-kb sequence, display a similar pattern with the same three units of repetition. A short signal derived from T17H1 (arrow) also was observed between the long telomere-proximal and middle T17H1 signals. (Bar = 20 μm.) (H) DNA fiber hybridized with the second mtDNA BAC T17H1 (green) and the third mtDNA BAC T18C6 (red). Signals derived from T18C6 also appear in triplicate. However, the centromere-proximal unit is longer than the other two. (Bar = 20 μm.) (I) DNA fiber hybridized with the fourth mtDNA BAC T5E7 (red) and centromere-proximal BAC T18A9 (green). The signal derived from T5E7 is not repeated. (Bar = 20 μm.) (J) Proposed structure of mitochondrial insertion locus and its relationship with the four mtDNA domains (the length of each repetitive unit is based on fiber-FISH data and is thus a representation of mean kilobase estimates). As in C, the green dots represent the two sets of specific repeats.