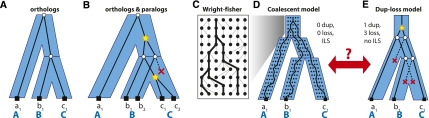
Figure 1.
Different views of gene trees and species trees. (A) In the dup-loss model, a congruent gene tree and species tree indicates that all genes are orthologs. (B) Incongruence indicates the presence of gene duplications (stars) and gene losses (red “X”). (C) An example of the Wright-Fisher (WF) process and the coalescence of three lineages within the population. (D) A multispecies coalescent is a combination of WF processes for each branch of the species tree. In this model, no duplications or losses are allowed, but a gene tree can be incongruent due to a phenomenon known as incomplete lineage sorting (ILS). (E) In the dup-loss model, the same gene tree in panel D can be explained using one gene duplication and at least three gene losses. ILS cannot be modeled in the dup-loss model.