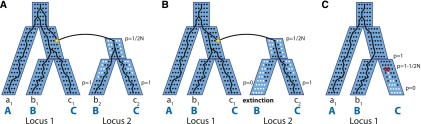
Figure 2.
Duplication and loss events within a multispecies coalescent. (A) A duplication occurs in one chromosome and creates a new locus, “locus 2,” in the genome. At locus 2, the Wright-Fisher model dictates how the frequency p of the daughter duplicate (black dots) competes with the null allele (white dots) until it eventually fixes (p = 1). A gene tree is therefore a “traceback” in this combined process. (B) A new duplicate can undergo hemiplasy, and fixes in some lineages and goes extinct in others. (C) Similar to duplication, a gene loss (deletion) starts in one chromosome and drifts until it fixes or goes extinct.