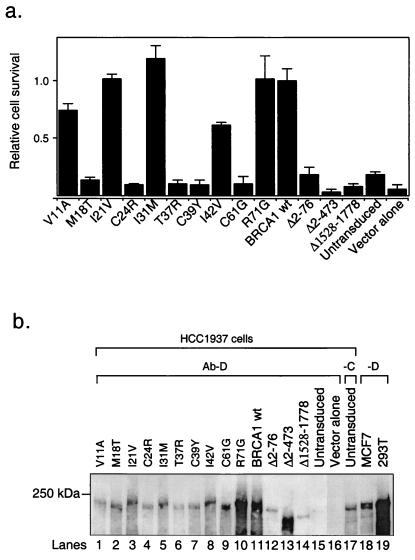
Figure 3.
Effect of BRCA1 RING mutations on protection from radiation hypersensitivity. HCC1937 cells were stably reconstituted with either wt BRCA1 or different mutants by using retroviral vectors. (a) Relative cell survival after IR. The mean values (and SEM) of the ratio of the number of colonies with and without IR are shown (1.0 is defined arbitrarily for the mean value of wt BRCA1). (b) Steady-state levels of the BRCA1 proteins in HCC1937 cells. BRCA1 was immunoprecipitated from lysates of cultures that were harvested at comparable confluence (between 70% and 100% confluent). MCF7 cells were only about 50% and 293T cells about 70% confluent when harvested; therefore, BRCA1 from MCF7 cells is relatively underrepresented (lane 18). BRCA1 was immunoprecipitated by using Ab-D (lanes 1–16) or Ab-C (lane 17) from lysates of HCC1937 cells or Ab-D from lysates of MCF7 (lane 18) and 293T cells (lane 19). All immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS/PAGE and analyzed by Western blot analysis using Ab SD 118. Lanes 1–10, individual missense mutations within the N terminus of BRCA1, as indicated; lane 11, wt BRCA1; lanes 12–14, truncated BRCA1 species used as controls; lanes 15 and 17, untransduced HCC1937 cells; lane 16, HCC1937 cells infected with the empty vector; and lanes 18 and 19, endogenous BRCA1 from MCF7 and 293T cells, respectively. The 250-kDa protein marker is indicated on the left.