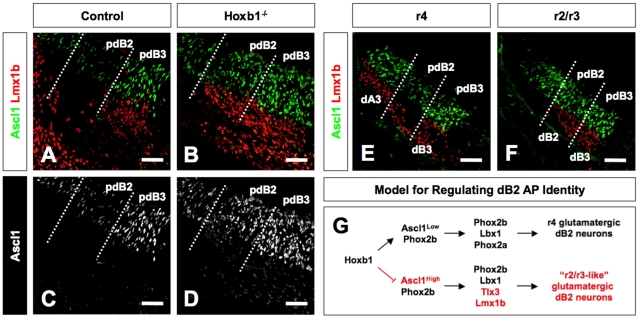
Figure 5. Hoxb1 modulates expression of Ascl1 in the dB2 progenitor domain at the level of r4.
(A–D) Transverse sections through r4 of E11.5 control and Hoxb1−/− embryos immunolabeled for Ascl1 and Lmx1b. In the control embryo, pdB2 expresses low levels of Ascl1 and no Lmx1b. In contrast, the expression of Ascl1 is increased and Lmx1b is ectopically produced from the pdB2 domain in the Hoxb1−/− embryo. Panels C and D show Ascl1 staining only for clarity. (E, F) Transverse section through r4 and r2/r3 of control E11.5 embryo immunolabeled for Ascl1 and Lmx1b. The pdB2 domain in r4 expresses low levels of Ascl1 with no postmitotic Lmx1b neurons differentiating from this domain. In contrast, the high level of Ascl1 expression in the pdB2 domain of r2/r3 is associated with differentiating Lmx1b neurons, an expression profile similar to r4 of Hoxb1−/− embryos. This suggests that in the absence of Hoxb1, the r4 pdB2 domain transforms into the more anterior r2/r3 pdB2 domain. (G) A model for regulating the AP identity of dB2 progenitors in r4. The pdB2 domain expresses low levels of Ascl1 and Phox2b (upper pathway). Postmitotic dB2 neurons emerge from the pdB2 domain expressing Phox2b, Lbx1, and Phox2a. As postmitotic dB2 neurons exit the pdB2 domain, they appear to migrate in a radial direction. In the absence of Hoxb1 (lower pathway), the expression of Phox2b within the pdB2 domain and glutamatergic markers among dB2 neurons appears unperturbed, whereas the expression of Ascl1 within the pdB2 domain is dramatically increased. This molecular phenotype is associated with the loss of Phox2a expression among postmitotic dB2 neurons and ectopic expression or de-repression of Tlx3 and Lmx1b from the pdB2. In the absence of Hoxb1, postmitotic dB2 neurons also appear to migrate in the ventromedial direction. These findings show the hallmark of a homeotic or anterior transformation (r4 dB2→r2/r3 dB2). This finding defines one of the earliest processes by which Hox genes regionally control the neurogenic program (Ascl1→Tlx3→glutamatergic neurons). However, it remains to be determined whether Hoxb1 directly regulates this pathway or via an intermediate molecule(s). Scale bars (A–F = 50 µm).