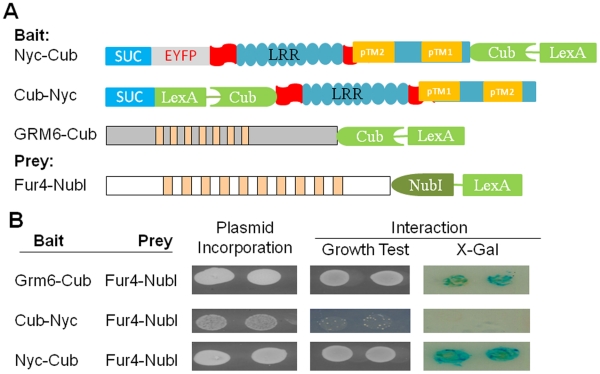
Figure 3. The N-terminus of nyctalopin is located in the extracellular space.
A. Schematic diagrams of constructs used to determine the orientation of nyctalopin in the yeast membrane. Bait constructs use the yeast invertase (SUC) signal sequence. In the schematic, the blue rectangle represents the invertase signal sequence (SUC), the grey rectangle EYFP, the aqua ovals each LRR domain, the aqua rectangle with predicted transmembrane (TM) domain (orange rectangle) , the chevron represents the C-terminus of ubiquitin (Cub) and the green rectangle represents the artificial transcription factor (VP16LexA). Cub-Nyc has CubLexAVP16 inserted between the SUC signal sequence and nyctalopin. B. Membrane yeast two hybrid analysis of nyctalopin orientation in the membrane. Plasmid incorporation (column 1) is confirmed by growth on SD/-LW plates. When NubI and CubLexAVP16 are both localized to the cytoplasm, interaction occurs and supports growth on SD/-LWHA media and expression of β-galactosidase. Grm6-Cub is used as a positive control. The lack of growth when Cub-Nyc and Fur4-NubI are co-expressed indicates that the N-terminus of nyctalopin is not in the cytoplasm. Growth and expression of β-galactosidase when Nyc-Cub and Fur4-NubI are co-transformed indicate the C-terminus of nyctalopin is localized in the cytoplasm.