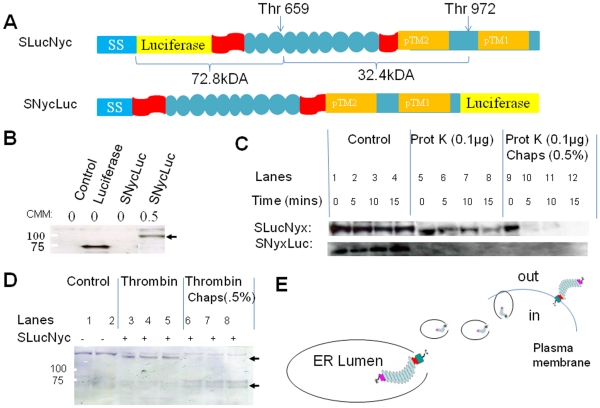
Figure 6. The N-terminus of nyctalopin is in the lumen of the ER.
A. Schematic of constructs used to determine the orientation of nyctalopin in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. SLucNyc (113 kDa) has luciferase (yellow rectangle) inserted after the murine nyctalopin signal sequence (SS). SNycLuc has luciferase attached to the C-terminus of full length nyctalopin. The arrows indicate the two thrombin (Thr) cleavage sites. Thrombin cleavage will generate 72.8 kDa and 34.4 kDa peptides, however, only the 72.8 kDa peptide will be labeled with biotinylated lysine and detected on a western blot. B. Western blot of in vitro transcription/translation reaction showing that without canine microsomal membranes (CMM), nyctalopin is not expressed. These data indicate co-translational processing and membrane insertion of nyctalopin in the ER. C. Expression of either SLucNyx or SNycLuc and treatment with proteinase K in the presence or absence of CHAPS. Lanes 1–4 indicate robust expression of full length nyctalopin. Lanes 5–8 show that SNycLuc but not SLucNyc is degraded by proteinase K, indicating the N-terminus of nyctalopin is in the ER lumen and therefore protected from degradation. Addition of CHAPS (0.5%) (lanes 9–12) disrupts the membranes and results in proteinase K digestion of both nyctalopin fusion proteins. D. Western blot of lysates from in vitro translation reactions, control (lanes 1–2), or when SLucNyc was included and after thrombin digestion alone (lanes 3–5) or thrombin digestion in the presence of 0.5% CHAPS (Lanes 6–8). Disruption of microsomal membranes with CHAPS allows cleavage of the fusion protein demonstrating that the N-terminus of nyctalopin is protected, and is therefore located in the lumen of the ER. Note the disappearance of the 113 kDa bands and the appearance of the 72 kDa band. E. Schematic showing a model of the orientation of nyctalopin in the ER and it’s subsequent disposition on the plasma membrane.