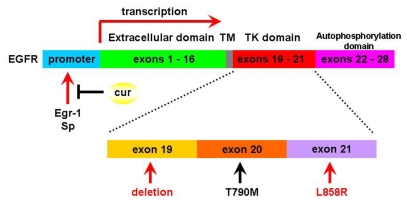
Figure 2.
The gene structure of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the genetic targets for curcumin and epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase (EGFR-TKIs). Exons 1–16 encode the EGFR extracellular domain (green), exons 17–18 encode the transmembrane domain (gray) and exons 19–21 encode the tyrosine kinase domain (red). Cancer cells harboring deletions in exon 19 or L858R mutation in exon 21 are sensitive to EGFR-TKIs (red arrows indicated). Secondary T790M mutation in exon 20 is a mechanism of acquired EGFR-TKIs resistance (black arrow indicated). Two transcription factors Egr-1 and Sp bind to EGFR gene promoter and accelerate EGFR mRNA transcription. Whereas curcumin attenuates Egr-1 and Sp binding and inhibites EGFR mRNA expressions.