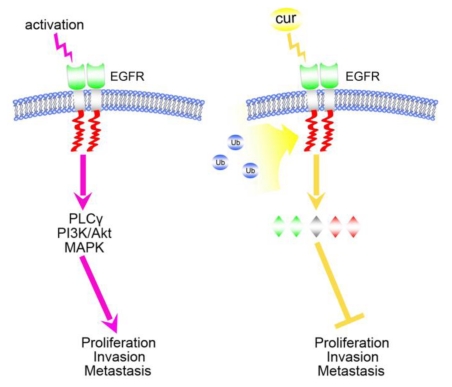
Figure 3.
Molecular mechanisms of EGFR-mediated cancer cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis. Upon activation, the extracellular domain of EGFR protein (green) transducts the signal into the intracellular tyrosine domain (red) through the transmembrane domain (gray). The PLCγ, PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways are subsequently activated, leading to cancer cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis. However, in the presence of curcumin, EGFR protein undergoes ubiquitination and degradation. Decreased EGFR protein on the cell membrane attenuates proliferative, invasive and metastatic signals, leading to cancer cell apoptosis and death. This mechanism works regardless of EGFR mutation status.