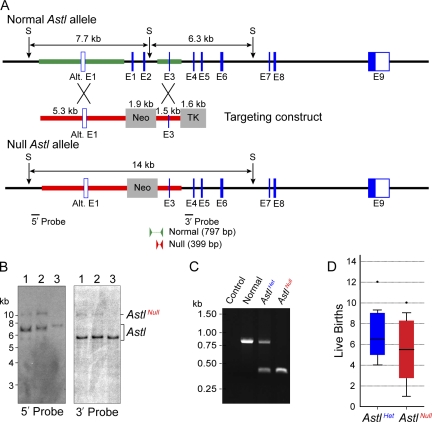
Figure 2.
Establishment of AstlNull mice. (A) A schematic of the normal and AstlNull alleles after targeting with a construct containing positive (phosphoglucokinase [PGK]-Neo) and negative (MC1-TK) selectable markers. The thicker lines represent the 5.3- and 1.5-kbp homologous arms that are 5′ and 3′, respectively, to the Neo cassette. 5′ (407 bp; 5 bp outside of the targeting construct) and 3′ (368 bp; 97 bp outside of the targeting construct) probes were used for Southern blot hybridization. Arrows indicate SspI (S) restriction endonuclease sites. PCR genotyping was performed using primers for the normal allele (797 bp) and null allele (399 bp). Alt., alternative. (B) Southern blot hybridization of ES cell DNA from two successfully targeted clones (1 and 2) and one normal control (3) detected the normal allele as 7.7- and 6.3-kbp fragments with the 5′ and 3′ 32P-labeled probes, respectively. The AstlNull allele was detected as a 14-kbp fragment with either the 5′ or the 3′ probe. (C) PCR genotyping of mouse tail DNA detected the normal (797 bp) and null (399 bp) Astl alleles. (D) The size of litters from AstlHet and AstlNull female mice (five per group) mated with normal males over a period of 8–10 mo. Box plots reflect the median (line) and data points within the 10th and 90th percentiles (error bars). Boxes include the middle two quartiles, and outliers are indicated by dots.