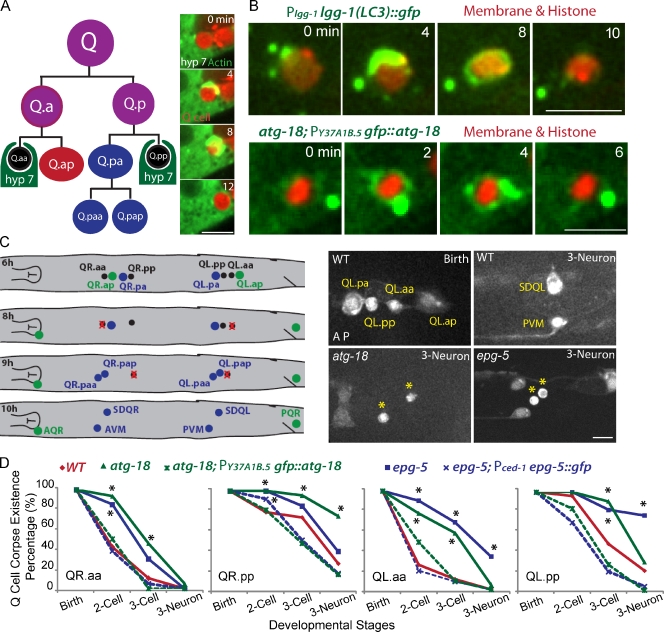
Figure 1.
C. elegans Q neuroblast apoptosis and the function of autophagy genes in Q cell corpse degradation. (A) The left cartoon shows the lineage of C. elegans Q neuroblasts and the phagocyte for Q cell corpse degradation. Three rounds of asymmetric cell divisions generate three neurons and two apoptotic cells (Q.aa and Q.pp). The neighboring epithelial cell, hyp7, engulfs and degrades the apoptotic Q cell. The right images show frames from time-lapse videos in which the GFP::actin cytoskeleton in the hyp7 cell forms an actin halo around the Q cell corpse (marked by cytosolic mCherry). More frames are shown in Fig. S1 A. (B) Still Images from videos show that autophagy markers GFP::LGG-1/LC3 (top) and GFP::ATG-18 (bottom) were recruited onto the outer surface of the Q cell corpse (red). Both markers were expressed under either the endogenous promoter for lgg-1 or hyp7 cell promoter for atg-18. The Q cell plasma membrane (mCherry with a myristoylation signal) and histone (his-24::mCherry) are shown in red. (C, left) The cartoon shows the developmental stage of Q cell at 6 h (birth of apoptotic Q cell), 8 h (two cell), 9 h (three cell), and 10 h (three neuron) after hatching. Definition is in the text (see The loss of autophagy genes delays Q cell corpse degradation section). Right images show Q cell corpse degradation in WT (top) or atg-18 (bottom left) or epg-5 mutant (bottom right). Asterisks show the ectopic Q cell corpses in autophagy mutants. Q cell names are adjacent. Genotypes are given in the top left. Developmental stages are given in the top right. Anterior of the cell is to the left. (D) Quantifications of Q cell corpse degradation in WT, atg-18 mutant, epg-5 mutant, or their rescue animals (dotted lines) at different Q cell developmental stages. *, P < 0.01, χ2 test. For each data point, n = 15–22 from a single experiment. Bars: (A and C) 5 µm; (B) 2.5 µm.