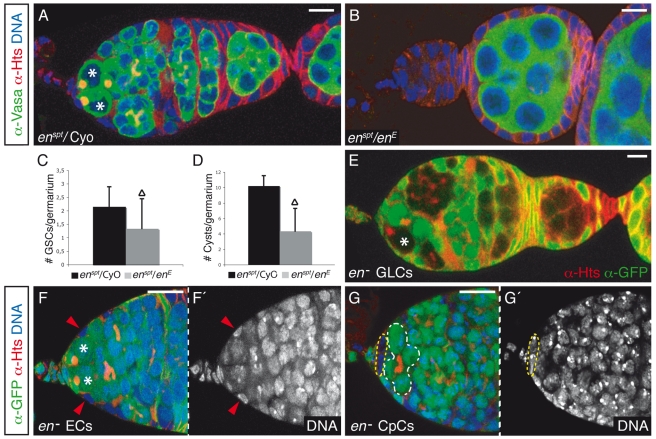
Figure 2. en controls germline development.
(A and B) Control (A) and experimental (B) germaria dissected after 7 d at restrictive temperature (28°C). While the control germarium shows two GSCs and several differentiating cysts, the mutant is devoid of germline cells. (C and D) Bar chart representations of the mean number of (C) GSCs (± standard deviation [s.d.]) and (D) cytoblasts and developing cysts (± s.d.) per germarium in control and experimental germaria. Triangles indicate statistically significant differences (Student's t test, p<0.0005). (E) en E germline clones dissected 21 d after heat shock. en is not required in the germline. (F) en E EC clones do not affect GSC maintenance. (G) en E CpCs induce GSC differentiation as shown by the appearance of branched fusomes adjacent to the mutant CpCs (see also Figure S2 and Table S1). Somatic clones were induced with the bab1-Gal4 driver and were dissected 3 d after eclosion. Asterisks, GSCs; GLCs, germline clones; yellow dashed lines, en mutant CpCs; white dashed line, four-cell cyst; red arrowheads, en mutant ECs. Scale bars: 10 µm.